Do women with high-risk HPV E6/E7 mRNA test positivity and NILM cytology need colposcopy?
- PMID: 37773080
- PMCID: PMC10542237
- DOI: 10.1186/s13027-023-00531-w
Do women with high-risk HPV E6/E7 mRNA test positivity and NILM cytology need colposcopy?
Erratum in
-
Correction: Do women with high-risk HPV E6/E7 mRNA test positivity and NILM cytology need colposcopy?Infect Agent Cancer. 2023 Dec 11;18(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s13027-023-00554-3. Infect Agent Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38082329 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to assess the value of an HPV E6/E7 mRNA assay and HPV 16 18/45 genotype assay combined with age stratification for triaging women negative for intraepithelial lesions or malignancy (NILM) cytology.
Methods: From January 2017 to December 2021, a total of 162,309 eligible women underwent cervical cancer screening at the Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, China. Excluding those with negative HPV E6/E7 mRNA, abnormal and unsatisfactory cytology, and those who failed to undergo colposcopy, 6,845 women were ultimately included in our study. We analysed the triage guidance for different subtypes of HPV in the presence of NILM cytology.
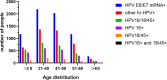
Results: Among 162,309 women, 19,834 (12.2%) were positive for HPV E6/E7 mRNA. Of the 6,845 women included in the study, 1,941 (28.4%), 561 (8.2%), 55 (0.8%) and 4,288 (62.6%) tested positive for HPV 16, HPV 18/45, HPV16/18/45 or other HR-HPV genotypes, respectively. The proportions of LSIL+ (including LSIL, HSIL and ICC) and HSIL+ (including HSIL and ICC) pathological results in the HPV 16/18/45 + group were 57% and 34.1%, respectively, higher than 36.3% and 11% in the other HR-HPV + group (χ2 = 653.214, P < 0.001). The percentages of LSIL + and HSIL + in the HPV16 + group (61.3% and 42.8%, respectively) and HPV16+/18/45 + group (76.3% and 41.9%, respectively) were much higher than those in the HPV18 + group (40.6% and 13.1%, respectively) (P < 0.001). However, there was no significant difference in the percentage of histopathological results between the HPV16 + group and HPV16+/18/45 + groups (P > 0.05). The above results were consistent after stratification according to age.
Conclusion: The rate of histopathological abnormalities was still high for the other HR-HPV subtypes with NILM cytology, although the rate of histopathological abnormalities was much higher for the HPV 16/18/45 positive subtypes. Therefore, colposcopy should be performed in women with HPV E6/E7 mRNA positivity and NILM cytology, regardless of age and HPV genotype.
Keywords: Cervical screening; Genotyping; HPV E6/E7 mRNA; NILM.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[HPV E6 and E7 mRNA combined with HPV 16 and 18 or 45 genotyping testing as a means of cervical cancer opportunistic screening].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2019 May 25;54(5):301-306. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567x.2019.05.003. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31154710 Chinese.
-
Diagnostic value of high-risk HPV E6/E7 mRNA in patients with ASCUS.BMC Womens Health. 2023 Sep 14;23(1):489. doi: 10.1186/s12905-023-02599-3. BMC Womens Health. 2023. PMID: 37710244 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical effect evaluation of high risk human papilloma virus E6/E7 mRNA in triaging women with atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2021 Oct 23;43(10):1094-1099. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20190516-00311. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34695901 Chinese.
-
[Comparative study of HR HPV E6/E7 mRNA and HR-HPV DNA in cervical cancer screening].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014 Nov 25;94(43):3432-5. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25622677 Chinese.
-
The clinical application of HPV E6/E7 mRNA testing in triaging women with atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance or low-grade squamous intra-epithelial lesion Pap smear: A meta-analysis.J Cancer Res Ther. 2017;13(4):613-620. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_56_17. J Cancer Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28901302 Review.
Cited by
-
Correction: Do women with high-risk HPV E6/E7 mRNA test positivity and NILM cytology need colposcopy?Infect Agent Cancer. 2023 Dec 11;18(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s13027-023-00554-3. Infect Agent Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38082329 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A et al. (2021): Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin, 71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Schiffman M, Rodriguez AC, Chen Z, Wacholder S, Herrero R, Hildesheim A, et al. A population-based prospective study of carcinogenic human papillomavirus variant lineages, viral persistence, and cervical neoplasia. Cancer Res. 2010;70:3159–69. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4179. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- M-2022242/Shandong Provincial Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Development Project
- M-2022242/Shandong Provincial Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Development Project
- 2020YXNS026,2021YXNS085,2022YXNS007/the Key R&D Program of Jining
- 2020YXNS026,2021YXNS085,2022YXNS007/the Key R&D Program of Jining
- 2020YXNS026,2021YXNS085,2022YXNS007/the Key R&D Program of Jining
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

