Chronic stress induces pulmonary epithelial cells to produce acetylcholine that remodels lung pre-metastatic niche of breast cancer by enhancing NETosis
- PMID: 37773152
- PMCID: PMC10540414
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-023-02836-5
Chronic stress induces pulmonary epithelial cells to produce acetylcholine that remodels lung pre-metastatic niche of breast cancer by enhancing NETosis
Abstract
Background: Chronic stress promotes most hallmarks of cancer through impacting the malignant tissues, their microenvironment, immunity, lymphatic flow, etc. Existing studies mainly focused on the roles of stress-induced activation of systemic sympathetic nervous system and other stress-induced hormones, the organ specificity of chronic stress in shaping the pre-metastatic niche remains largely unknown. This study investigated the role of chronic stress in remodeling lung pre-metastatic niche of breast cancer.
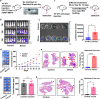
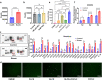
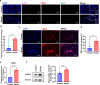
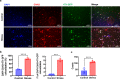
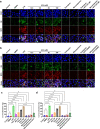
Methods: Breast cancer mouse models with chronic stress were constructed by restraint or unpredictable stress. Expressions of tyrosine hydroxylase, vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT), EpCAM and NETosis were examined by immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy. mRNA and protein levels of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), VAChT, and peptidylarginine deiminase 4 were detected by qRT-PCR and Western blotting, respectively. Immune cell subsets were analyzed by flow cytometry. Acetylcholine (ACh) and chemokines were detected by ELISA and multi chemokine array, respectively. ChAT in lung tissues from patients was examined by immunohistochemistry.
Results: Breast cancer-bearing mice suffered chronic stress metastasized earlier and showed more severe lung metastasis than did mice in control group. VAChT, ChAT and ChAT+ epithelial cells were increased significantly in lung of model mice undergone chronic stress. ACh and chemokines especially CXCL2 in lung culture supernatants from model mice with chronic stress were profoundly increased. Chronic stress remodeled lung immune cell subsets with striking increase of neutrophils, enhanced NETosis in lung and promoted NETotic neutrophils to capture cancer cells. ACh treatment resulted in enhanced NETosis of neutrophils. The expression of ChAT in lung tissues from breast cancer patients with lung metastasis was significantly higher than that in patients with non-tumor pulmonary diseases.
Conclusions: Chronic stress promotes production of CXCL2 that recruits neutrophils into lung, and induces pulmonary epithelial cells to produce ACh that enhances NETosis of neutrophils. Our findings demonstrate for the first time that chronic stress induced epithelial cell derived ACh plays a key role in remodeling lung pre-metastatic niche of breast cancer.
Keywords: Acetycholine; Breast cancer; Chronic stress; Lung metastasis; NETosis; Neutrophils.
© 2023. Italian National Cancer Institute ‘Regina Elena’.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Wang YH, Li JQ, Shi JF, Que JY, Liu JJ, Lappin JM, et al. Depression and anxiety in relation to cancer incidence and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(7):1487–99. - PubMed
-
- Cui B, Peng F, Lu J, He B, Su Q, Luo H, et al. Cancer and stress: NextGen strategies. Brain Behav Immun. 2021;93:368–83. - PubMed
-
- Yang H, Xia L, Chen J, Zhang S, Martin V, Li Q, et al. Stress-glucocorticoid-TSC22D3 axis compromises therapy-induced antitumor immunity. Nat Med. 2019;25(9):1428–41. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81520108024/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81872317/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81930079/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- WKJ-ZJ-1803/Health Commission of Zhejiang Province
- 2019R01007/Leading Innovative and Entrepreneur Team Introduction Program of Zhejiang Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

