Insights on Covid-19 with superimposed pulmonary histoplasmosis: The possible nexus
- PMID: 37773721
- PMCID: PMC10540147
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.989
Insights on Covid-19 with superimposed pulmonary histoplasmosis: The possible nexus
Abstract
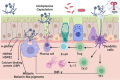
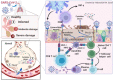
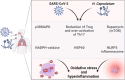
A novel coronavirus (CoV) known as severe acute respiratory syndrome CoV type 2 is the causative agent for the development of CoV disease 2019 (Covid-19). Covid-19 may increase the risk of developing pulmonary histoplasmosis due to immune dysregulation. In addition, Covid-19 may enhance the propagation of acute pulmonary histoplasmosis due to lung injury and inflammation, and using corticosteroids in severely affected Covid-19 patients may reactivate latent pulmonary histoplasmosis. Likewise, activation of inflammatory signaling pathways during H. capsulatum infection may increase the severity of Covid-19 and vice versa. Furthermore, lymphopenia in Covid-19 may increase the risk for the progress of pulmonary histoplasmosis besides activation of inflammatory signaling pathways during H. capsulatum infection may increase the severity of Covid-19 and vice versa. Therefore, this critical review aimed to find the potential link between Covid-19 pneumonia and pulmonary histoplasmosis concerning the immunological response.
Keywords: Covid-19; inflammatory signaling pathways; pulmonary histoplasmosis.
© 2023 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical