Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is a biomarker for predicting patients with sepsis
- PMID: 37773726
- PMCID: PMC10541755
- DOI: 10.1177/03000605231202139
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is a biomarker for predicting patients with sepsis
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the potential value of serum hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) concentrations as a biomarker in patients with sepsis.
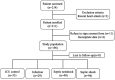
Methods: The enrolled patients were divided into the following four groups: the intensive care unit (ICU) control group (n = 33), infection group (n = 29), septic nonshock group (n = 40), and septic shock group (n = 94). An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to measure serum HIF-1α concentrations on ICU admission. Clinical parameters and laboratory test results were also collected.
Results: Serum HIF-1α concentrations were significantly higher in the infection group, septic nonshock group, and septic shock group than in the ICU control group. Moreover, HIF-1α concentrations were associated with a better predictive ability for diagnosing sepsis than the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II score, procalcitonin concentrations, and lactate concentrations. Patients with sepsis and HIF-1α concentrations >161.14 pg/mL had a poor prognosis.
Conclusions: Serum HIF-1α concentrations are a useful biomarker for the diagnosis of sepsis and predicting the prognosis of patients.
Keywords: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II; Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; biomarker; intensive care unit; lactate; sepsis; septic shock.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Van der Poll T, Van de Veerdonk FL, Scicluna BP, et al. The immunopathology of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Immunol 2017; 17: 407–420. 2017/04/25. DOI: 10.1038/nri.2017.36. - PubMed
-
- Weng L, Zeng XY, Yin P, et al. Sepsis-related mortality in China: a descriptive analysis. Intensive Care Med 2018; 44: 1071–1080. 2018/05/31. DOI: 10.1007/s00134-018-5203-z. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

