Scalable inference of cell differentiation networks in gene therapy clonal tracking studies of haematopoiesis
- PMID: 37774002
- PMCID: PMC10585354
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btad605
Scalable inference of cell differentiation networks in gene therapy clonal tracking studies of haematopoiesis
Abstract
Motivation: Investigating cell differentiation under a genetic disorder offers the potential for improving current gene therapy strategies. Clonal tracking provides a basis for mathematical modelling of population stem cell dynamics that sustain the blood cell formation, a process known as haematopoiesis. However, many clonal tracking protocols rely on a subset of cell types for the characterization of the stem cell output, and the data generated are subject to measurement errors and noise.
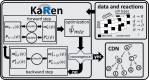
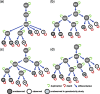
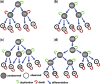
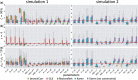
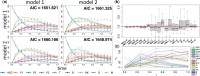
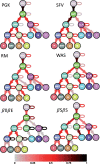
Results: We propose a stochastic framework to infer dynamic models of cell differentiation from clonal tracking data. A state-space formulation combines a stochastic quasi-reaction network, describing cell differentiation, with a Gaussian measurement model accounting for data errors and noise. We developed an inference algorithm based on an extended Kalman filter, a nonlinear optimization, and a Rauch-Tung-Striebel smoother. Simulations show that our proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art and scales to complex structures of cell differentiations in terms of nodes size and network depth. The application of our method to five in vivo gene therapy studies reveals different dynamics of cell differentiation. Our tool can provide statistical support to biologists and clinicians to better understand cell differentiation and haematopoietic reconstitution after a gene therapy treatment. The equations of the state-space model can be modified to infer other dynamics besides cell differentiation.
Availability and implementation: The stochastic framework is implemented in the R package Karen which is available for download at https://cran.r-project.org/package=Karen. The code that supports the findings of this study is openly available at https://github.com/delcore-luca/CellDifferentiationNetworks.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Bobo D, Lipatov M, Rodriguez-Flores JL et al. False negatives are a significant feature of next generation sequencing callsets. bioRxiv, 10.1101/066043, 2016, preprint: not peer reviewed. - DOI
-
- Burnham KP, Anderson DR, Huyvaert KP et al. AIC model selection and multimodel inference in behavioral ecology: some background, observations, and comparisons. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 2011;65:23–35. 10.1007/s00265-010-1029-6. - DOI
-
- Cooper GM, Adams K. The Cell: A Molecular Approach. New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 2023.
-
- Del Core L. The stochastic route of haematopoiesis: modelling and inference methods in clonal tracking studies. PhD Thesis, University of Groningen, 2023. 10.33612/diss. - DOI

