Aquatic plant wax hydrogen and carbon isotopes in Greenland lakes record shifts in methane cycling during past Holocene warming
- PMID: 37774023
- PMCID: PMC10541501
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adh9704
Aquatic plant wax hydrogen and carbon isotopes in Greenland lakes record shifts in methane cycling during past Holocene warming
Abstract
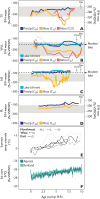
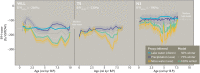
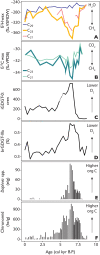
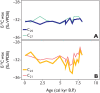
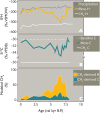
Predicting changes to methane cycling in Arctic lakes is of global concern in a warming world but records constraining lake methane dynamics with past warming are rare. Here, we demonstrate that the hydrogen isotopic composition (δ2H) of mid-chain waxes derived from aquatic moss clearly decouples from precipitation during past Holocene warmth and instead records incorporation of methane in plant biomass. Trends in δ2Hmoss and δ13Cmoss values point to widespread Middle Holocene (11,700 to 4200 years ago) shifts in lake methane cycling across Greenland during millennia of elevated summer temperatures, heightened productivity, and lowered hypolimnetic oxygen. These data reveal ongoing warming may lead to increases in methane-derived C in many Arctic lakes, including lakes where methane is not a major component of the C cycle today. This work highlights a previously unrecognized mechanism influencing δ2H values of mid-chain wax and draws attention to the unquantified role of common aquatic mosses as a potentially important sink of lake methane across the Arctic.
Figures

References
-
- Wik M., Varner R. K., Anthony K. W., MacIntyre S., Bastviken D., Climate-sensitive northern lakes and ponds are critical components of methane release. Nat. Geosci. 9, 99–105 (2016).
-
- M. Collins, R. Knutti, J. Arblaster, T. Fichefet, P. Friedlingstein, X. Gao, W. J. Gutowski, T. Johns, G. Krinner, M. Shongwe, C. Tebaldi, A. J. Weaver, M. Wehner, 2013: Long-term Climate Change: Projections, Commitments and Irreversibility, in Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group 1 to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, T.F. Stocker, D. Qin, G.-K.Plattner, M. Tignor, S.K. Allen, J. Boschung, A. Nauels, Y. Xia, V. Bex and P.M. Midgley, Eds. (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2014), pp. 1029–1136.
-
- Verpoorter C., Kutser T., Seekell D. A., Tranvik L. J., A global inventory of lakes based on high-resolution satellite imagery. Geophys. Res. Lett. 41, 6396–6402 (2014).
-
- Wik M., Thornton B. F., Bastviken D., MacIntyre S., Varner R. K., Crill P. M., Energy input is primary controller of methane bubbling in subarctic lakes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 41, 555–560 (2014).
-
- Walter K. M., Smith L. C., Chapin F. S., Methane bubbling from northern lakes: Present and future contributions to the global methane budget. Philos. Trans. Royal Soc. A. 365, 1657–1676 (2007). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

