Oral Cancer Prediction Using a Probability Neural Network (PNN)
- PMID: 37774049
- PMCID: PMC10762769
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.9.2991
Oral Cancer Prediction Using a Probability Neural Network (PNN)
Abstract
Objective: In India, usually, oral cancer is mostly identified at a progressive stage of malignancy. Hence, we are motivated to identify oral cancer in its early stages, which helps to increase the lifetime of the patient, but this early detection is also more challenging.
Methods: The proposed research work uses a probabilistic neural network (PNN) for the prediction of oral malignancy. The recommended work uses PNN along with the discrete wavelet transform to predict the cancer cells accurately. The classification accuracy of the PNN model is 80%, and hence this technique is best for the prediction of oral cancer.
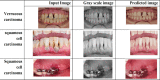
Result: Due to heterogeneity in the appearance of oral lesions, it is difficult to identify the cancer region. This research work explores the different computer vision techniques that help in the prediction of oral cancer.
Conclusion: Oral screening is important in making a decision about oral lesions and also in avoiding delayed referrals, which reduces mortality rates.
Keywords: Discrete wavelet Transform (DWT); Malignancy; Probabilistic Neural Network (PNN); early detection; oral cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Heidari AE, Sunny Sumsum P, James Bonney L, et al. Optical Coherence Tomography as an Oral Cancer Screening Adjunct in a Low Resource Settings. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron. 2019:25.
-
- Hu Z, Alsadoon A, Manoranjan P, et al. Early-Stage Oral Cavity Cancer Detection: Anisotropic Pre-Processing and Fuzzy C-Means Segmentation. 2018:8–10.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical