Diagnosis and management of ventricular tachycardia
- PMID: 37775174
- PMCID: PMC10541285
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmed.2023-23.5.Cardio3
Diagnosis and management of ventricular tachycardia
Abstract
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) describes rapid heart rhythms originating from the ventricles. Accurate diagnosis of VT is important to allow prompt referral to specialist services for ongoing management. The diagnosis of VT is usually made based on electrocardiographic data, most commonly 12-lead echocardiography (ECG), as well as supportive cardiac telemetric monitoring. Distinguishing between VT and supraventricular arrhythmias on ECG can be difficult. However, the VT diagnosis frequently needs to be made rapidly in the acute setting. In this review, we discuss the definition of VT, review features of wide-complex tachycardia (WCT) on ECG that might be helpful in diagnosing VT, discuss the different substrates in which VT can occur and offer brief comments on management considerations for patients found to have VT.
Keywords: ECG; Ventricular tachycardia; ablation; arrhythmia; wide-complex tachycardia.
© Royal College of Physicians 2023. All rights reserved.
Figures
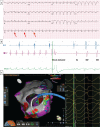


References
-
- McAlpine WA. Heart and coronary arteries. Berlin; Springer, 1975.
-
- Kapa S, Gaba P, Desimone CV, Asirvatham SJ. Fascicular ventricular arrhythmias: pathophysiologic mechanisms, anatomical constructs, and advances in approaches to management. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2017;10:e002476. - PubMed
-
- Christoffels VM, Moorman AFM. Development of the cardiac conduction system. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2009;2:195–207. - PubMed
-
- Virágh SZ, Challice CE. The development of the conduction system in the mouse embryo heart. Dev Biol 1977;56:397–411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

