High-resolution Imaging Using Virtual-Pinhole PET Concept
- PMID: 37775372
- PMCID: PMC10840911
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cpet.2023.08.002
High-resolution Imaging Using Virtual-Pinhole PET Concept
Abstract
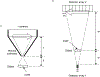
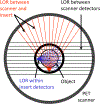
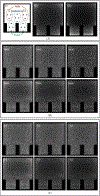
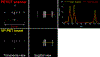
Organ-specific PET scanners continues to draw interest for their high-resolution imaging capability that is unmatched by whole-body PET/computed tomography (CT) scanners. The virtual-pinhole PET concept offers new opportunities in PET system design, allowing one to mix and match detectors of different characteristics to achieve the highest performance such as high image resolution, high system sensitivity, and large imaging field-of-view. This novel approach delivers high-resolution PET images previously available only through organ-specific PET scanner while maintaining the imaging field-of-view of a clinical PET/CT scanner to see the entire body.
Keywords: Organ-specific PET imaging; PET; Positron emission tomography; Virtual-pinhole PET; Zoom-in PET imaging.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


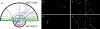

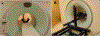


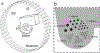

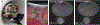

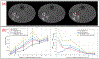
References
-
- Gallagher BM, Ansari A, Atkins H, et al. Radiopharmaceuticals XXVII. 18F-labeled 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-d-glucose as a radiopharmaceutical for measuring regional myocardial glucose metabolism in vivo: tissue distribution and imaging studies in animals. J. Nucl. Med 1977;18(10):990–6 - PubMed
-
- Kuhl DE, Phelps ME, Hoffman EJ, Robinson GD Jr., MacDonald NS. Initial clinical experience with 18F-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose for determination of local cerebral glucose utilization by emission computed tomography. Acta Neurol. Scand. Suppl 1977;64:192–3 - PubMed
-
- Gallagher BM, Fowler JS, Gutterson NI, MacGregor RR, Wan CN, Wolf AP. Metabolic trapping as a principle of oradiopharmaceutical design: some factors resposible for the biodistribution of [18F] 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-glucose. J. Nucl. Med 1978;19(10):1154–61 - PubMed
-
- Som P, Atkins HL, Bandoypadhyay D, et al. A fluorinated glucose analog, 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose (F-18): nontoxic tracer for rapid tumor detection. J. Nucl. Med 1980;21(7):670–5 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

