Research trends in readiness for hospital discharge between 2002 and 2021: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 37775985
- PMCID: PMC10643845
- DOI: 10.1002/nop2.2009
Research trends in readiness for hospital discharge between 2002 and 2021: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Aim: This study aimed to undertake a bibliometric analysis to provide comprehensive information in demonstrating the current status and outline the overall trends in the area of readiness for hospital discharge (RHD).
Design: A bibliometric and visual analysis of RHD literature was undertaken.
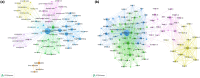
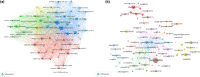
Methods: Articles were retrieved from the Web of Science network from 2002 to 2021. VOSviewer was used to identify the co-authorship network of countries/institutions, co-authorship and co-citation analysis of authors, and co-citation analysis of references and citation analysis of documents. CiteSpace was used to identify the keyword co-occurrence network and perform cluster analysis, detecting the keywords with citation bursts and speculated frontiers in this research field.
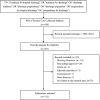
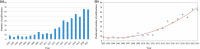
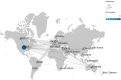
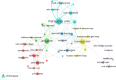
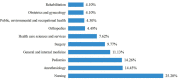
Results: A total of 512 articles were included in the final analysis. Key findings are: (1) There has been a continuous but somewhat fluctuating rise in the number of publications. (2) 56.05% of publications come from the USA with Marquette University making the highest contribution. (3) Most publications (17, 3.32%) in RHD research were from the Journal of Clinical Nursing, and Anaesthesia and Analgesia had the highest number of citations (584 citations). (4) Weiss ME (25, 4.88%) was the most productive author whose articles have been the most highly cited (646 citations). (5) Cited references from Weiss ME (2007) also made the largest contribution to co-citations, and the most cited reference was from Jack BW (2009) (1022 citations). (6) The 20 most frequent keywords and keywords with the strongest citation bursts were retrieved. There were seven research hotspots, and three emerging research frontiers were explored.
Conclusions: The bibliometric analysis of material published in the last 20 years indicates that there have been statistically significant gains in comprehensive information on RHD, including the knowledge mapping of the countries, institutions, authors, references and keywords. The hotspots and frontiers, which have been explored can give guidance to researchers as to new angles and directions to take.
Implications for nursing management: The effects of the implementation of ERAS on RHD-related risk for adverse post-discharge outcomes in surgical patients will be of increasing concern for healthcare professionals. It is important for patients and their relatives to be confident that on discharge they are sufficiently ready for hospital discharge to enable them to safely and smoothly make the transition to home. Improving the level of RHD in discharged patients can help nurse managers and researchers measure the effectiveness of discharge planning services.
Keywords: CiteSpace; VOSviewer; bibliometric analysis; health care; length of stay; readiness for hospital discharge.
© 2023 The Authors. Nursing Open published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors have declared no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

