Is the Current Cut Point for Glycated Haemoglobin (HbA1c) Correct for Diagnosing Diabetes Mellitus in Premenopausal Women? Evidence to Inform Discussion
- PMID: 37777677
- PMCID: PMC10786809
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-023-01482-6
Is the Current Cut Point for Glycated Haemoglobin (HbA1c) Correct for Diagnosing Diabetes Mellitus in Premenopausal Women? Evidence to Inform Discussion
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Is the Current Cut Point for Glycated Haemoglobin (HbA1c) Correct for Diagnosing Diabetes Mellitus in Premenopausal Women? Evidence to Inform Discussion.Diabetes Ther. 2024 Feb;15(2):565-566. doi: 10.1007/s13300-023-01498-y. Diabetes Ther. 2024. PMID: 38038899 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
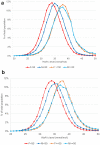
Introduction: Women are on average diagnosed with diabetes mellitus at later age than men but have higher mortality. As the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus is primarily based on HbA1c, the use of a non-specific reference range and cut point for diabetes mellitus that does not account for gender differences in diabetes could potentially lead to underdiagnosis of diabetes mellitus in women and missed opportunities for intervention. We investigated whether a contributing factor to the later diagnosis in women may be a difference in distribution of HbA1c in premenopausal women versus men of the same age by comparing HbA1c values in men and women across multiple sites in the UK.
Methods: We analysed the HbA1c levels of 146,907 individuals who underwent single testing only and had HbA1c ≤ 50 mmol/mol between 2012 and 2019 in one laboratory (cohort 1). This was replicated in six laboratories with 938,678 individuals tested between 2019 and 2021 (cohort 2).
Results: In cohort 1, women < 50 years old had an HbA1c distribution markedly lower than that in men by a mean of 1.6 mmol/mol (p < 0.0001), while the difference in the distribution of HbA1c for individuals aged ≥ 50 years was less pronounced (mean difference 0.9 mmol/mol, p < 0.0001). For individuals under the age of 50, HbA1c in women lagged by up to 10 years compared to men. Similar findings were found in cohort 2. We estimated an additional 17% (n = 34,953) of undiagnosed women aged < 50 years in England and Wales could be reclassified to have diabetes mellitus, which may contribute to up to 64% of the difference in mortality rates between men/women with diabetes mellitus aged 16-50 years.
Conclusion: The HbA1c cut point for diagnosis of diabetes mellitus may need to be re-evaluated in women under the age of 50 years. Early identification of diabetes mellitus in women has the potential to improve women's health outcomes in the longer term.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Diagnostic controversies; Epidemiology; Haemoglobin A1c; Sex difference.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare: no support from any organisation for the submitted work; no financial relationships with any organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes around the world in 2021. https://diabetesatlas.org/. Accessed 3 May 2023.
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials