NADH elevation during chronic hypoxia leads to VHL-mediated HIF-1α degradation via SIRT1 inhibition
- PMID: 37777750
- PMCID: PMC10543270
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-023-01130-3
NADH elevation during chronic hypoxia leads to VHL-mediated HIF-1α degradation via SIRT1 inhibition
Abstract
Background: Under conditions of hypoxia, cancer cells with hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) from heterogeneous tumor cells show greater aggression and progression in an effort to compensate for harsh environmental conditions. Extensive study on the stability of HIF-1α under conditions of acute hypoxia in cancer progression has been conducted, however, understanding of its involvement during the chronic phase is limited.
Methods: In this study, we investigated the effect of SIRT1 on HIF1 stability in a typical chronic hypoxic conditon that maintains cells for 24 h under hypoxia using Western blotting, co-IP, measurement of intracellular NAD + and NADH levels, semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis, invasion assay, gene knockdown.
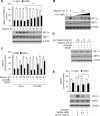
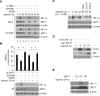
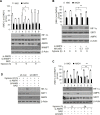
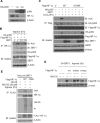
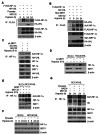
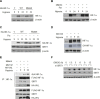
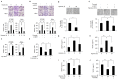
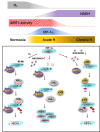
Results: Here we demonstrated that the high concentration of pyruvate in the medium, which can be easily overlooked, has an effect on the stability of HIF-1α. We also demonstrated that NADH functions as a signal for conveyance of HIF-1α degradation via the SIRT1 and VHL signaling pathway under conditions of chronic hypoxia, which in turn leads to attenuation of hypoxically strengthened invasion and angiogenic activities. A steep increase in the level of NADH occurs during chronic hypoxia, leading to upregulation of acetylation and degradation of HIF-1α via inactivation of SIRT1. Of particular interest, p300-mediated acetylation at lysine 709 of HIF-1α is recogonized by VHL, which leads to degradation of HIF-1α via ubiquitin/proteasome machinary under conditions of chronic hypoxia. In addition, we demonstrated that NADH-elevation-induced acetylation and subsequent degradation of HIF-1α was independent of proline hydroxylation.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest a critical role of SIRT1 as a metabolic sensor in coordination of hypoxic status via regulation of HIF-1α stability. These results also demonstrate the involvement of VHL in degradation of HIF-1α through recognition of PHD-mediated hydroxylation in normoxia and p300-mediated HIF-1α acetylation in hypoxia.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Chronic hypoxia; HIF-1α degradation; Invasion; NADH elevation; SIRT1; VHL.
© 2023. Society of Chinese Bioscientists in America (SCBA).
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has any competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ascorbate modulates the hypoxic pathway by increasing intracellular activity of the HIF hydroxylases in renal cell carcinoma cells.Hypoxia (Auckl). 2019 May 15;7:17-31. doi: 10.2147/HP.S201643. eCollection 2019. Hypoxia (Auckl). 2019. PMID: 31192266 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1 deacetylates and stabilizes hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) via direct interactions during hypoxia.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Jul 10;462(4):294-300. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.04.119. Epub 2015 May 13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 25979359
-
Accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is limited by transcription-dependent depletion.Oncogene. 2005 Jul 14;24(30):4829-38. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208636. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15897903
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1)alpha: its protein stability and biological functions.Exp Mol Med. 2004 Feb 29;36(1):1-12. doi: 10.1038/emm.2004.1. Exp Mol Med. 2004. PMID: 15031665 Review.
-
Regulation of the SIAH2-HIF-1 Axis by Protein Kinases and Its Implication in Cancer Therapy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 25;9:646687. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.646687. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33842469 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lactylation: A Novel Post-Translational Modification with Clinical Implications in CNS Diseases.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 19;14(9):1175. doi: 10.3390/biom14091175. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of acetylation and deacetylation in cancer metabolism.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Jan;15(1):e70145. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70145. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39778006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 (HIF-1) in Cancer: Emerging Therapeutic Strategies and Pathway Regulation.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Feb 1;17(2):195. doi: 10.3390/ph17020195. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) Ameliorates Free Fatty Acid-Induced Pancreatic β-Cell Dysfunction via the NAD+/AMPK/SIRT1/HIF-1α Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 30;25(19):10534. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910534. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408861 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic and comprehensive insights into HIF-1 stabilization under normoxic conditions: implications for cellular adaptation and therapeutic strategies in cancer.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jan 6;30(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00682-7. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 39757165 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hockel M, et al. Association between tumor hypoxia and malignant progression in advanced cancer of the uterine cervix. Cancer Res. 1996;56(19):4509–15. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

