The development of proximity labeling technology and its applications in mammals, plants, and microorganisms
- PMID: 37777761
- PMCID: PMC10544124
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-023-01310-1
The development of proximity labeling technology and its applications in mammals, plants, and microorganisms
Erratum in
-
Correction: The development of proximity labeling technology and its applications in mammals, plants, and microorganisms.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Aug 16;22(1):403. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01750-3. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39152415 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
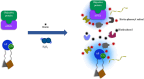
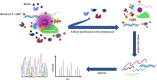
Protein‒protein, protein‒RNA, and protein‒DNA interaction networks form the basis of cellular regulation and signal transduction, making it crucial to explore these interaction networks to understand complex biological processes. Traditional methods such as affinity purification and yeast two-hybrid assays have been shown to have limitations, as they can only isolate high-affinity molecular interactions under nonphysiological conditions or in vitro. Moreover, these methods have shortcomings for organelle isolation and protein subcellular localization. To address these issues, proximity labeling techniques have been developed. This technology not only overcomes the limitations of traditional methods but also offers unique advantages in studying protein spatial characteristics and molecular interactions within living cells. Currently, this technique not only is indispensable in research on mammalian nucleoprotein interactions but also provides a reliable approach for studying nonmammalian cells, such as plants, parasites and viruses. Given these advantages, this article provides a detailed introduction to the principles of proximity labeling techniques and the development of labeling enzymes. The focus is on summarizing the recent applications of TurboID and miniTurbo in mammals, plants, and microorganisms. Video Abstract.
Keywords: APEX; BioID; Proximity labeling; TurboID; miniTurbo.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

