Antiviral efficacy of molnupiravir versus ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir in patients with early symptomatic COVID-19 (PLATCOV): an open-label, phase 2, randomised, controlled, adaptive trial
- PMID: 37778363
- PMCID: PMC7615401
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00493-0
Antiviral efficacy of molnupiravir versus ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir in patients with early symptomatic COVID-19 (PLATCOV): an open-label, phase 2, randomised, controlled, adaptive trial
Erratum in
-
Correction to Lancet Infect Dis 2023; published online Sept 28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00493-0.Lancet Infect Dis. 2023 Dec;23(12):e511. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00649-7. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Lancet Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37839427 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Molnupiravir and ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir are the two leading oral COVID-19 antiviral treatments, but their antiviral activities in patients have not been compared directly. The aim of this ongoing platform trial is to compare different antiviral treatments using the rate of viral clearance as the measure of antiviral effect.
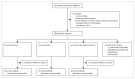
Methods: PLATCOV is an open-label, multicentre, phase 2, randomised, controlled, adaptive pharmacometric platform trial running in Thailand, Brazil, Pakistan, and Laos. The component of the trial reported here was conducted in the Hospital for Tropical Diseases, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand. We recruited low-risk adult patients aged 18-50 years with early symptomatic COVID-19 (<4 days of symptoms). Eligible patients were randomly assigned using block randomisation via a centralised web app to one of seven treatment groups: molnupiravir, ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir, casirivimab-imdevimab, tixagevimab-cilgavimab, favipiravir, fluoxetine, or no study drug. The no study drug group comprised a minimum proportion of 20% of patients at all times, with uniform randomisation ratios applied across the active treatment groups. Results for the concurrently randomised molnupiravir, ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir, and no study drug groups are reported here. The primary endpoint was the rate of oropharyngeal viral clearance assessed in a modified intention-to-treat population, defined as patients with more than 2 days of follow-up. Safety was assessed in all participants who took at least one dose of the medication. The viral clearance rate was derived under a Bayesian hierarchical linear model fitted to the log10 viral densities in standardised duplicate oropharyngeal swab eluates taken daily over 1 week (18 measurements). Treatment groups with a probability of more than 0·9 that viral clearance was accelerated by more than 20% compared with no drug entered a non-inferiority comparison (with a 10% non-inferiority margin) compared with the platform's current most effective drug. This ongoing trial is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT05041907.
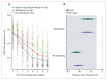
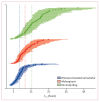
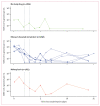
Findings: Between June 6, 2022, and Feb 23, 2023, 209 patients in Thailand were enrolled and concurrently randomly assigned to molnupiravir (n=65), ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir (n=59), or no study drug (n=85). 129 (62%) of the patients were female and 80 (38%) were male. Relative to the no study drug group, the rates of viral clearance were 37% (95% credible interval 16-65) faster with molnupiravir and 84% (54-119) faster with ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir. In the non-inferiority comparison, viral clearance was 25% (10-38) slower with molnupiravir than ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir. Molnupiravir was removed from the study platform when it reached the prespecified inferiority margin of 10% compared with ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir. Median estimated viral clearance half-lives were 8·5 h (IQR 6·7-10·1) with ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir, 11·6 h (8·6-15·4) with molnupiravir, and 15·5 h (11·9-21·2) with no study drug. Viral rebound occurred more frequently following nirmatrelvir (six [10%] of 58) compared with the no study drug (one [1%] of 84; p=0·018) or the molnupiravir (one [2%] of 65; p=0·051) groups. Persistent infections following molnupiravir had more viral mutations (three of nine patients had an increased number of single nucleotide polymorphisms in samples collected at 7 or more days compared with those at baseline) than after nirmatrelvir (zero of three) or no study drug (zero of 19). There were no adverse events of grade 3 or worse, or serious adverse events in any of the reported treatment groups.
Interpretation: Both molnupiravir and ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir accelerate oropharyngeal SARS-CoV-2 viral clearance in patients with COVID-19, but the antiviral effect of ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir was substantially greater. Measurement of oropharyngeal viral clearance rates provides a rapid and well tolerated approach to the assessment and comparison of antiviral drugs in patients with COVID-19. It should be evaluated in other acute viral respiratory infections.
Funding: Wellcome Trust through the COVID-19 Therapeutics Accelerator.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests We declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

