Cleavage kinetics of human mitochondrial RNase P and contribution of its non-nuclease subunits
- PMID: 37779095
- PMCID: PMC10602865
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad713
Cleavage kinetics of human mitochondrial RNase P and contribution of its non-nuclease subunits
Abstract
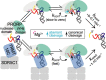
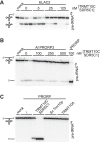
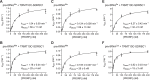
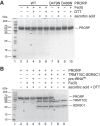
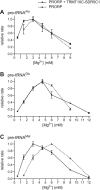
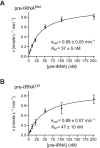
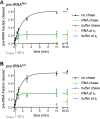
RNase P is the endonuclease responsible for the 5' processing of precursor tRNAs (pre-tRNAs). Unlike the single-subunit protein-only RNase P (PRORP) found in plants or protists, human mitochondrial RNase P is a multi-enzyme assembly that in addition to the homologous PRORP subunit comprises a methyltransferase (TRMT10C) and a dehydrogenase (SDR5C1) subunit; these proteins, but not their enzymatic activities, are required for efficient pre-tRNA cleavage. Here we report a kinetic analysis of the cleavage reaction by human PRORP and its interplay with TRMT10C-SDR5C1 including 12 different mitochondrial pre-tRNAs. Surprisingly, we found that PRORP alone binds pre-tRNAs with nanomolar affinity and can even cleave some of them at reduced efficiency without the other subunits. Thus, the ancient binding mode, involving the tRNA elbow and PRORP's PPR domain, appears basically retained by human PRORP, and its metallonuclease domain is in principle correctly folded and functional. Our findings support a model according to which the main function of TRMT10C-SDR5C1 is to direct PRORP's nuclease domain to the cleavage site, thereby increasing the rate and accuracy of cleavage. This functional dependence of human PRORP on an extra tRNA-binding protein complex likely reflects an evolutionary adaptation to the erosion of canonical structural features in mitochondrial tRNAs.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The protein-only RNase Ps, endonucleases that cleave pre-tRNA: Biological relevance, molecular architectures, substrate recognition and specificity, and protein interactomes.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2024 Mar-Apr;15(2):e1836. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1836. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2024. PMID: 38453211 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular recognition of pre-tRNA by Arabidopsis protein-only Ribonuclease P.RNA. 2017 Dec;23(12):1860-1873. doi: 10.1261/rna.061457.117. Epub 2017 Sep 5. RNA. 2017. PMID: 28874505 Free PMC article.
-
Bi-allelic variants in the mitochondrial RNase P subunit PRORP cause mitochondrial tRNA processing defects and pleiotropic multisystem presentations.Am J Hum Genet. 2021 Nov 4;108(11):2195-2204. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.10.002. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Am J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 34715011 Free PMC article.
-
Of P and Z: mitochondrial tRNA processing enzymes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Sep-Oct;1819(9-10):1017-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.11.003. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22137969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Dynamic Network of RNP RNase P Subunits.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 24;22(19):10307. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910307. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638646 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TRMT10C-mediated m7G modification of circFAM126A inhibits lung cancer growth by regulating cellular glycolysis.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Sep 18;40(1):78. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09918-w. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39289194 Free PMC article.
-
The protein-only RNase Ps, endonucleases that cleave pre-tRNA: Biological relevance, molecular architectures, substrate recognition and specificity, and protein interactomes.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2024 Mar-Apr;15(2):e1836. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1836. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2024. PMID: 38453211 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of 3'-tRNA maturation by the human mitochondrial RNase Z complex.EMBO J. 2024 Dec;43(24):6573-6590. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00297-w. Epub 2024 Nov 8. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 39516281 Free PMC article.
-
FASTKD5 processes mitochondrial pre-mRNAs at noncanonical cleavage sites.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jul 8;53(13):gkaf665. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf665. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40637235 Free PMC article.
-
Tangled but ordered human mitochondrial tRNA maturation.Sci China Life Sci. 2025 Jan 14. doi: 10.1007/s11427-024-2782-1. Online ahead of print. Sci China Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39825210 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

