Marine natural product lepadin A as a novel inducer of immunogenic cell death via CD91-dependent pathway
- PMID: 37779162
- PMCID: PMC10542626
- DOI: 10.1007/s13659-023-00401-3
Marine natural product lepadin A as a novel inducer of immunogenic cell death via CD91-dependent pathway
Abstract
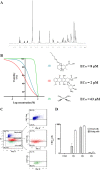
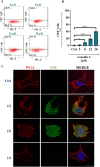
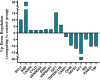
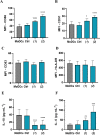
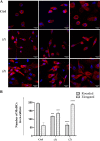
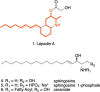
Immunogenic Cell Death (ICD) represents a mechanism of enhancing T cell-driven response against tumor cells. The process is enabled by release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and cytokines by dying cells. Based on molecular studies and clinical marker assessment, ICD can be a new target for cancer chemotherapy hitherto restricted to a few conventional anticancer drugs. In view of the development of small molecules in targeted cancer therapy, we reported the preliminary evidence on the role of the natural product lepadin A (1) as a novel ICD inducer. Here we describe the ICD mechanism of lepadin A (1) by proving the translocation of the protein calreticulin (CRT) to the plasma membrane of human A2058 melanoma cells. CRT exposure is an ICD marker in clinical studies and was associated with the activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway in A2058 cells with lepadin A (1). After the treatment, the tumour cells acquired the ability to activate dendritic cells (DCs) with cytokine release and costimulatory molecule expression that is consistent with a phenotypic profile committed to priming T lymphocytes via a CD91-dependent mechanism. The effect of lepadin A (1) was dose-dependent and comparable to the response of the chemotherapy drug doxorubicin (2), a well-established ICD inducer.
Keywords: Anticancer; Drug discovery; Immunogenic cell death; Immunotherapy; Natural products.
© 2023. Kunming Institute of Botany, CAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Natural Compounds of Marine Origin as Inducers of Immunogenic Cell Death (ICD): Potential Role for Cancer Interception and Therapy.Cells. 2021 Jan 25;10(2):231. doi: 10.3390/cells10020231. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33504012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stimulators of immunogenic cell death for cancer therapy: focusing on natural compounds.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Sep 13;23(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03058-7. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37705051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromomycin A5 induces bona fide immunogenic cell death in melanoma.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 9;13:941757. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.941757. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36439184 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the Marine Alkaloid Lepadin A as Potential Inducer of Immunogenic Cell Death.Biomolecules. 2022 Feb 2;12(2):246. doi: 10.3390/biom12020246. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204747 Free PMC article.
-
Inducing enhanced immunogenic cell death with nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems for pancreatic cancer therapy.Biomaterials. 2016 Sep;102:187-97. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.06.032. Epub 2016 Jun 18. Biomaterials. 2016. PMID: 27343466
Cited by
-
Clinical application of immunogenic cell death inducers in cancer immunotherapy: turning cold tumors hot.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 May 7;12:1363121. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1363121. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38774648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Standardized sulforhodamine b colorimetric cell proliferation assay for anticancer activity screening in educational and research laboratories.MethodsX. 2025 Jun 30;15:103469. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2025.103469. eCollection 2025 Dec. MethodsX. 2025. PMID: 40687356 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

