Emergence of Pulmonary Tuberculosis While Recovering From COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Case Report
- PMID: 37779797
- PMCID: PMC10540490
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.44398
Emergence of Pulmonary Tuberculosis While Recovering From COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Case Report
Abstract
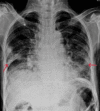
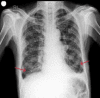
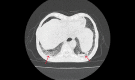
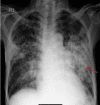
COVID-19 can have different presentations; from asymptomatic to multiorgan involvement. This case report is of an elderly gentleman, with known comorbidities of chronic obstructive airway disease and alcoholic liver disease on treatment. He presented with a history of increasing dyspnea and cough for a few days which was present after cold symptoms, and was admitted for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia. Later, while he was recovering from COVID-19 pneumonia, his respiratory symptoms worsened. After a thorough evaluation, his sputum smear was positive for acid-fast bacilli and also rifampicin sensitive on GeneXpert assay. With timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, he recovered from both acute conditions and was sent home on the twentieth day of admission.
Keywords: copd (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease); covid 19; covid pneumonia; hospital-acquired pneumonia; tb: tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2023, Shrestha et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
API TB Consensus Guidelines 2006: Management of pulmonary tuberculosis, extra-pulmonary tuberculosis and tuberculosis in special situations.J Assoc Physicians India. 2006 Mar;54:219-34. J Assoc Physicians India. 2006. PMID: 16800350
-
COMPARISON OF GeneXpert MTB/RIF ASSAY WITH CONVENTIONAL AFB SMEAR FOR DIAGNOSIS OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND.Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2017 Mar;48(2):313-21. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2017. PMID: 29641882
-
COVID-19 pneumonia with pulmonary tuberculosis: Double trouble.Int J Mycobacteriol. 2021 Apr-Jun;10(2):206-209. doi: 10.4103/ijmy.ijmy_51_21. Int J Mycobacteriol. 2021. PMID: 34558477
-
Use of steroids to treat anti-tumor necrosis factor α induced tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: Case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Oct 23;99(43):e22076. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022076. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33120729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Agranulocytosis due to anti-tuberculosis drugs including isoniazid (INH) and rifampicin (RFP)--a report of four cases and review of the literature].Kekkaku. 2003 Nov;78(11):683-9. Kekkaku. 2003. PMID: 14672045 Review. Japanese.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
