Is there a role in acute kidney injury for FGF23 and Klotho?
- PMID: 37779849
- PMCID: PMC10539225
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfad093
Is there a role in acute kidney injury for FGF23 and Klotho?
Abstract
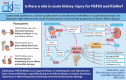
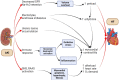
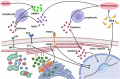
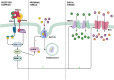
Cardio-renal syndrome is a clinical condition that has recently been well defined. In acute kidney disease, this interaction might trigger chronic processes determining the onset of cardiovascular events and the progression of chronic kidney disease. Moreover, the high mortality rate of acute kidney injury (AKI) is also linked to the fact that this condition is often complicated by dysfunctions of other organs such as lungs or heart, or is associated with septic episodes. In this context the role and the potential link between bone, heart and kidney is becoming an important topic of research. The aim of this review is to describe the cardiac alterations in the presence of AKI (cardiorenal syndrome type 3) and explore how bone can interact with heart and kidney in determining and influencing the trend of AKI in the short and long term. The main anomalies of mineral metabolism in patients with AKI will be reported, with specific reference to the alterations of fibroblast growth factor 23 and Klotho as a link between the bone-kidney-heart axis.
Keywords: CKDMBD; FGF23; Klotho; acute kidney injury; mineral metabolism.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Conflict of interest statement
J.B. is member of the CKJ editorial board. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Klotho in AKI.Semin Nephrol. 2019 Jan;39(1):57-75. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2018.10.005. Semin Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 30606408 Review.
-
Urine Klotho Is Lower in Critically Ill Patients With Versus Without Acute Kidney Injury and Associates With Major Adverse Kidney Events.Crit Care Explor. 2019 Jun;1(6):e0016. doi: 10.1097/cce.0000000000000016. Crit Care Explor. 2019. PMID: 32123869 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor-23-Klotho Axis in Cardiorenal Syndrome: Mediators and Potential Therapeutic Targets.Front Physiol. 2021 Nov 15;12:775029. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.775029. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34867481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Klotho relieves inflammation and exerts a cardioprotective effect during renal ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiorenal syndrome.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Sep;153:113515. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113515. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36068956
-
The FGF23-Klotho axis and cardiac tissue Doppler imaging in pediatric chronic kidney disease-a prospective cohort study.Pediatr Nephrol. 2018 Jan;33(1):147-157. doi: 10.1007/s00467-017-3766-5. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 28795324 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Associations of Intact and C-Terminal FGF23 with Inflammatory Markers in Older Patients Affected by Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 6;13(13):3967. doi: 10.3390/jcm13133967. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38999530 Free PMC article.
-
Neurofibromatosis type I (NF1) and bone involvement in a pediatric setting: insights from FGF23 levels.Ital J Pediatr. 2025 Mar 25;51(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s13052-025-01941-9. Ital J Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40133996 Free PMC article.
-
Osteosarcopenia in Chronic Kidney Disease: An Overlooked Syndrome?J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2025 Apr;16(2):e13787. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13787. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2025. PMID: 40192621 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kellum JA, Lameire N, Aspelin Pet al. . Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int Suppl 2012;2:1–138.
-
- Scaravilli V, Merrino A, Bichi Fet al. . Longitudinal assessment of renal function after lung transplantation for cystic fibrosis: transition from post-operative acute kidney injury to acute kidney disease and chronic kidney failure. J Nephrol 2022;35:1885–93. 10.1007/s40620-022-01392-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

