Therapeutic Potential of Antiviral Peptides against the NS2B/NS3 Protease of Zika Virus
- PMID: 37779969
- PMCID: PMC10536883
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c04903
Therapeutic Potential of Antiviral Peptides against the NS2B/NS3 Protease of Zika Virus
Abstract
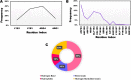
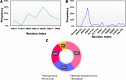
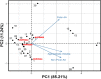
The NS2B/NS3 protease is highly conserved among various proteases of the Zika virus, making it an important therapeutic target for developing broad-spectrum antiviral drugs. The NS2B/NS3 protease is a crucial enzyme in the replication cycle of Zika virus and plays a significant role in viral maturation and assembly. Inhibiting the activity of this protease can potentially prevent viral replication, making it an attractive target for developing therapies against Zika virus infection. This work screens 429 antiviral peptides in comparison with substrate peptide against the NS2B/NS3 of Zika virus using molecular docking and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation. Based on the docking screening, MD simulation conducted for the best four peptides including AVP0239, AVP0642, AVP0660, and AVP2044, could be effective against NS2B/NS3. These results were compared with the control substrate peptide. Further analysis indicates that AVP0642 and AVP2044 are the most promising candidates. The interaction analysis showed that the catalytic site residues including His51, Asp75, Ser135 and other non-catalytic residues such as Asp129, Asp83, and Asp79 contribute substantial interactions. Hydrogen bonds (41%) and hydrophobic interactions (33%) are observed as the prominent non-covalent interaction prompting the peptide-protein complex formation. Furthermore, the structure-activity relationship (SAR) illustrates that positively charged (Lys, Arg) residues in the peptides dominate the interactions. This study provides the basis for developing novel peptide-based protease inhibitors for Zika virus.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Investigating into the molecular interactions of flavonoids targeting NS2B-NS3 protease from ZIKA virus through in-silico approaches.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021 Jan;39(1):272-284. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2019.1709546. Epub 2020 Jan 10. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021. PMID: 31920173
-
Structures and dynamics of peptide and peptidomimetic inhibitors bound to the NS2B-NS3 protease of the ZIKA virus.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023 Apr;41(7):3076-3088. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2022.2045223. Epub 2022 Mar 3. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023. PMID: 35238272
-
Investigating Lycotoxin-An1a (An1a), a defense antiviral peptide from Alopecosa nagpag venom as prospective anti-dengue agent against DENV-2 NS2B-NS3 protease.Comput Biol Chem. 2024 Feb;108:108005. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2023.108005. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Comput Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38157660
-
Advances in Computational Methods to Discover New NS2B-NS3 Inhibitors Useful Against Dengue and Zika Viruses.Curr Top Med Chem. 2022;22(29):2435-2462. doi: 10.2174/1568026623666221122121330. Curr Top Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36415099 Review.
-
NS2B-NS3 protease inhibitors as promising compounds in the development of antivirals against Zika virus: A systematic review.J Med Virol. 2022 Feb;94(2):442-453. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27386. Epub 2021 Oct 20. J Med Virol. 2022. PMID: 34636434
Cited by
-
Exploring the therapeutic potential of DV-B-120 as an inhibitor of dengue virus infection.J Virol. 2024 Apr 16;98(4):e0125823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01258-23. Epub 2024 Mar 28. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38546211 Free PMC article.
-
Computational analysis of antimicrobial peptides targeting key receptors in infection-related cardiovascular diseases: molecular docking and dynamics insights.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 14;15(1):8896. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93683-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40087360 Free PMC article.
-
iDNS3IP: Identification and Characterization of HCV NS3 Protease Inhibitory Peptides.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 3;26(11):5356. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115356. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508165 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances on Targeting Proteases for Antiviral Development.Viruses. 2024 Feb 27;16(3):366. doi: 10.3390/v16030366. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38543732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Employing Machine Learning-Based QSAR for Targeting Zika Virus NS3 Protease: Molecular Insights and Inhibitor Discovery.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Aug 15;17(8):1067. doi: 10.3390/ph17081067. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choudhry H.; Alzahrani F. A.; Hassan M. A.; Alghamdi A.; Abdulaal W. H.; Bakhrebah M. A.; Zamzami M. A.; Helmi N.; Bokhari F. F.; Zeyadi M.; Baothman O. A.; Kamal M. A.; Warsi M. K.; Ali A.; Jarullah B.; Jamal M. S. Zika Virus Targeting by Screening Inhibitors against NS2B/NS3 Protease. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 3947245 10.1155/2019/3947245. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

