The effect of heat-moisture treatment changed the binding of starch, protein and lipid in rice flour to affect its hierarchical structure and physicochemical properties
- PMID: 37780235
- PMCID: PMC10534091
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.100785
The effect of heat-moisture treatment changed the binding of starch, protein and lipid in rice flour to affect its hierarchical structure and physicochemical properties
Abstract
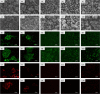
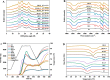
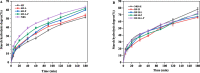
This study investigated the effect of removing proteins, lipids and starch on the structure, physicochemical properties and digestion properties of rice flour (with 30% moisture) treated with heat moisture treatment (HMT). According to the results, HMT caused the adhesion and agglomeration of the rice flour, promoted the binding between starch, protein and lipid molecular chains and led to the formation of complexes (especially starch-lipid complexes), which hindered the removal of non-starch components. Compared to the untreated rice flour, the HMT treated lipid-removal rice flour had small changes in their crystallinity, gelatinization temperature and viscosity property. After removing protein, the crystallinity, peak viscosity, final viscosity, breakdown and starch digestibility were sharply increased. In particular, the peak viscosity increased from 811 cP to 1746 cP and the enthalpy change increased from 5.33 J/g to 10.18 J/g. These findings are helpful in understanding the contribution of removing endogenous proteins and lipids to the physicochemical changes of HMT treated rice flour during its heating process and thus can be helpful in controlling the quality of rice flour through HMT.
Keywords: Heat-moisture treatment; Lipids; Physicochemical properties; Proteins; Rice flour; Starch digestibility.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- AACC. (2000). Approved methods of the American association of cereal chemists. In). St. Paul, MN, USA: AACC International.
-
- Arslan F.N., Akin G., Karuk Elmas Ş.N., Üner B., Yilmaz I., Janssen H.-G., Kenar A. FT-IR spectroscopy with chemometrics for rapid detection of wheat flour adulteration with barley flour. Journal of Consumer Protection and Food Safety. 2020;15(3):245–261. doi: 10.1007/s00003-019-01267-9. - DOI
-
- Dhital S., Brennan C., Gidley M.J. Location and interactions of starches in planta: Effects on food and nutritional functionality. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2019;93:158–166. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.09.011. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

