Targeted metabolic reveals different part of maize in polyphenolic metabolites during germination and hypoglycemic activity analysis
- PMID: 37780325
- PMCID: PMC10534241
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.100848
Targeted metabolic reveals different part of maize in polyphenolic metabolites during germination and hypoglycemic activity analysis
Abstract
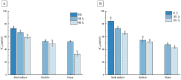
In this study, qualitative and quantitative analyses of phenolic compounds in the maize germinating seed embryo, radicle, and germ were performed at 0, 48, and 96 h post-germination, followed by the evaluation of their hypoglycemic activity. The results revealed the accumulation of 80 phenolics in different parts of germinated maize, of which 47, 48, and 53 were present in the seed embryo, radicle, and germ. After germination 22, 26, and 34 polyphenols were found to differential accumulate in the seed embryo, radicle, and germ. At 96 h post-germination, the content of monomeric phenols in the germ was higher than that in the radicle and seed embryo. Moreover, the inhibitory activity of polyphenols in the germ towards α-glucosidase and α-amylase was higher than that in the radicle and seed embryo. These results indicate that germination can effectively improve the type and content of phenolic compounds in different parts of maize.
Keywords: Hypoglycemic activity; Maize germination; Phenolic compound; Seed part.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of Reactive Oxygen Scavenger N,N'-Dimethylthiourea (DMTU) on Seed Germination and Radicle Elongation of Maize.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 25;24(21):15557. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115557. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958543 Free PMC article.
-
Storage behavior of Chionanthus retusus seed and asynchronous development of the radicle and shoot apex during germination in relation to germination inhibitors, including abscisic acid and four phenolic glucosides.Plant Cell Physiol. 2004 Sep;45(9):1158-67. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pch129. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15509838
-
Stimulation of Phenolics, Antioxidant and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activities During Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Seed Germination.Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2016 Jun;71(2):211-7. doi: 10.1007/s11130-016-0549-2. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27188780
-
Phenolic compounds in germinated cereal and pulse seeds: Classification, transformation, and metabolic process.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020;60(5):740-759. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1550051. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020. PMID: 30633553 Review.
-
A review of the seed biology of Paeonia species (Paeoniaceae), with particular reference to dormancy and germination.Planta. 2019 Feb;249(2):291-303. doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-3017-4. Epub 2018 Oct 1. Planta. 2019. PMID: 30276471 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization of microwave parameters to enhance phytochemicals, antioxidants and metabolite profile of de-oiled rice bran.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 14;14(1):23959. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74738-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39397141 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into characteristic metabolites and potential bioactive peptides profiles of fresh cheese fermented with three novel probiotics based metabolomics and peptidomics.Food Chem X. 2024 Jan 18;21:101147. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101147. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Food Chem X. 2024. PMID: 38312486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilar J., Miano A.C., Obregón J., Soriano-Colchado J., Barraza-Jáuregui G. Malting process as an alternative to obtain high nutritional quality quinoa flour. Journal of Cereal Science. 2019;90 doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2019.102858. - DOI
-
- Carreño-Carrillo C.V., Sánchez E.V., Verduzco C.-P., J e. Polyphenol-based nuclear magnetic resonance non-targeted metabolomics of temperature- and time-controlled blue and red maize sprouting. SN Applied Sciences. 2021;3:300. doi: 10.1007/s42452-021-04171-w. - DOI
-
- Chen X.X., Jiao J.Y., Cao W.X., Yu B.G., Liu Y.M., Zou C.Q. A sustainable phosphorus management in agriculture: Assessing trade-offs between human health risks and nutritional yield regarding heavy metals in maize grain. Environmental Research. 2022;203 doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111792. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

