Factors affecting caregivers' participation in support groups for people living with HIV in Tanzania
- PMID: 37780441
- PMCID: PMC10540687
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1215219
Factors affecting caregivers' participation in support groups for people living with HIV in Tanzania
Abstract
Introduction: Support groups for people living with HIV (PLHIV) are essential for increasing adherence, retention, addressing their psychosocial needs and improving patient literacy. However, factors that influence participation of caregivers living with HIV (LHIV) in these groups are scarcely documented, particularly for those caring for orphans and vulnerable children (OVC).
Methods: This study used baseline data collected between 1st October 2021 and 30th September 2022 from the PEPFAR/USAID-funded Adolescents and Children HIV Incidence Reduction, Empowerment and Virus Elimination (ACHIEVE) project in Tanzania to investigate factors that affect participation of caregivers LHIV in support groups for PLHIV. A total of 74,249 HIV-positive OVC caregivers who were already receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) and had a confirmed care and treatment centre identification number were included in the analysis. Factors affecting group participation were identified through multilevel analysis using multivariable mixed-effects logistic regression.
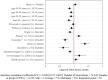
Results: Results showed that 84.2% of the caregivers were participants in the support groups for PLHIV. Their mean age was 36 years, and the majority (82.1%) were female. Multivariable analysis revealed that participation in the groups was more likely among caregivers living in urban areas (aOR = 1.39 [1.24, 1.55]), with primary education (aOR = 1.17 [1.07, 1.28]), and without disabilities (aOR = 0.62 [0.47, 0.82]). However, participation was less likely among widowed (aOR = 0.91 [0.84, 0.999]), single or unmarried (aOR = 0.86 [0.78, 0.95]), and those with secondary education or higher levels than never attended (aOR = 0.69 [0.60, 0.80]), moderate hunger (aOR = 0.86 [0.79, 0.93]), and those aged 30 years or older (p< 0.001).
Discussion: A sizeable proportion (15.8%) of the caregivers were not in support groups for PLHIV, ranging from 12.3% among those in households with severe hunger to 29.7% among disabled ones. The study highlights the need for tailored interventions to increase participation in support groups for PLHIV, particularly for caregivers who are disabled, live in rural areas, are older, widowed, and/or unmarried, and those in poor households.
Keywords: HIV; Tanzania; caregivers; membership; support groups for people living with HIV.
Copyright © 2023 Kikoyo, Exavery, Charles, Temu, Barankena, Ally, Mseya, Mbwambo, Fovo, Tarimo, Mubyazi, Balampama, Kuhlik, Ventimiglia and Lema.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mazambara F, Chagwena D, Mudzviti T, Sithole S, Monera-Penduka T, Maponga CC, et al. Utility of HIV support groups in advancing implementation research in resource-limited settings: experiences from an urban-setting HIV support group in Zimbabwe. AIDS Res Ther. (2022) 19:7. doi: 10.1186/s12981-022-00431-w - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- PEPFAR . Ariel adherence clubs: Increasing retention in care and adherence to life-saving antiretroviral therapy among children and adolescents living with HIV in Tanzania. PEPFAR solutions platform (BETA). (2018). Available at: https://www.pepfarsolutions.org/solutions/2018/1/13/ariel-adherence-club... (Accessed 12 December 2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

