Hotspots and future trends of autophagy in Traditional Chinese Medicine: A Bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 37780780
- PMCID: PMC10539644
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20142
Hotspots and future trends of autophagy in Traditional Chinese Medicine: A Bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Objective: To discuss the hotspots and future trends of autophagy in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and provide a reference for researchers in this field.
Method: Using visual analysis tools, metrological statistics and visual research on the pertinent literature in the area of autophagy use in TCM were undertaken in the core collection database of the Web of Science. By examining the authors, keywords, research circumstances, research hotspots, and trends of linked research, the use of autophagy in TCM was investigated.
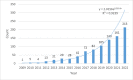
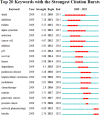
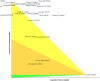
Results and conclusions: A total of 916 studies were included, among which Beijing University Chinese Medicine was the largest number of advantageous research institutions, followed by Shanghai University Traditional Chinese Medicine and Guangzhou University Chinese Medicine.The keywords of literature research primarily comprise apoptosis, activation, inhibition, pathway, mechanism, oxidative stress, proliferation, NF-κB, cancer, mtor, etc. At present, the research on autophagy in the field of TCM is increasing on a year-to-year basis. The research has focused on the role played by TCM in malignant tumors, atherosclerosis, Alzheimer's disease through autophagy, and the regulation of autophagy signaling pathways (e.g., PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, TLR4 signaling pathway,nrf2 signaling pathway and NF-κB signaling pathway). In the future, the therapeutic effect of TCM on chemotherapy-resistant tumor cells through autophagy pathway, the role of TCM mediating mitophagy and activating autophagy function, and the therapeutic effect of TCM components represented by luteolin on tumors, asthma, myocardial injury and other diseases through autophagy mechanism will be the research hotspots in the future.
Keywords: Autophagy; Bibliometrics analysis; CiteSpace; Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM); Visualized Analysis.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Bibliometric analysis of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease.Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2024 May 1;52(3):31-41. doi: 10.15586/aei.v52i3.1047. eCollection 2024. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2024. PMID: 38721953
-
[Visual analysis of research on traditional Chinese medicine treatment of Alzheimer's disease in recent ten years].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Mar;48(6):1673-1681. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20221206.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37005855 Review. Chinese.
-
Exploring global research status and trends in anti-obesity effects of traditional Chinese medicine through intestinal microbiota: a bibliometric study.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Nov 16;13:1271473. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1271473. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38045760 Free PMC article.
-
The interactions between traditional Chinese medicine and gut microbiota: Global research status and trends.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Sep 12;12:1005730. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1005730. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36171760 Free PMC article.
-
The Traditional Chinese Medicine in Treating Diabetic Nephropathy: A Bibliometric Analysis.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 Oct 4;17:4627-4636. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S482473. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 39381421 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Global research hotspots and trends of Buyang huanwu decoction: A visual analysis of the literature based on CiteSpace.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 8;103(45):e40457. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040457. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39533635 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of autophagy‑related genes in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.Exp Ther Med. 2024 Sep 25;28(6):440. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12729. eCollection 2024 Dec. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 39355520 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric and visual analysis in the field of macrophages in Traditional Chinese Medicine from 2003 to 2023.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 2;16:1558926. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1558926. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40242756 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Z.Y., Liu J., Zhu Z., et al. Traditional Chinese medicine compounds regulate autophagy for treating neurodegenerative disease: a mechanism review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021 Jan;133 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

