Role of the vaginal microbiome in miscarriage: exploring the relationship
- PMID: 37780845
- PMCID: PMC10533927
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1232825
Role of the vaginal microbiome in miscarriage: exploring the relationship
Abstract
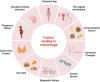
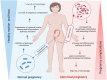
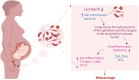
Miscarriage is a devastating pregnancy loss that affects many women worldwide. It is characterized as a spontaneous miscarriage that occurs before 20 weeks of gestation which affects more than 25% of pregnancies. While the causes of miscarriage are complex and multifactorial, recent research has suggested a potential role of the vaginal microbiota. The vaginal microbiome is a dynamic ecosystem of microbes that are essential for preserving vaginal health and avoiding infections. Vaginal dysbiosis has been accompanied with numerous adverse pregnancy complications, such as preterm birth. However, the effect of the vaginal microbiome in miscarriage is not fully understood. This review aims to investigate the link between vaginal microbiota and miscarriage. Also, we investigate the various mechanisms through which the vaginal microbiota may affect miscarriage. Additionally, we examine the implications of these research findings, specifically the possibility of vaginal microbiome screening and targeted interventions to prevent miscarriage.
Keywords: inflammation; pregnancy complications; pregnancy loss; vaginal dysbiosis; vaginal microbiota.
Copyright © 2023 Saadaoui, Singh, Ortashi and Al Khodor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adapen C., Reot L., Menu E. (2022). Role of the human vaginal microbiota in the regulation of inflammation and sexually transmitted infection acquisition: Contribution of the non-human primate model to a better understanding? Front. Reprod. Health 4, 992176. doi: 10.3389/frph.2022.992176 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

