An F-ratio-based method for estimating the number of active sources in MEG
- PMID: 37780957
- PMCID: PMC10537939
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1235192
An F-ratio-based method for estimating the number of active sources in MEG
Abstract
Introduction: Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a powerful technique for studying the human brain function. However, accurately estimating the number of sources that contribute to the MEG recordings remains a challenging problem due to the low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), the presence of correlated sources, inaccuracies in head modeling, and variations in individual anatomy.
Methods: To address these issues, our study introduces a robust method for accurately estimating the number of active sources in the brain based on the F-ratio statistical approach, which allows for a comparison between a full model with a higher number of sources and a reduced model with fewer sources. Using this approach, we developed a formal statistical procedure that sequentially increases the number of sources in the multiple dipole localization problem until all sources are found.
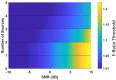
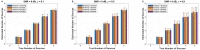
Results: Our results revealed that the selection of thresholds plays a critical role in determining the method's overall performance, and appropriate thresholds needed to be adjusted for the number of sources and SNR levels, while they remained largely invariant to different inter-source correlations, translational modeling inaccuracies, and different cortical anatomies. By identifying optimal thresholds and validating our F-ratio-based method in simulated, real phantom, and human MEG data, we demonstrated the superiority of our F-ratio-based method over existing state-of-the-art statistical approaches, such as the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) and Minimum Description Length (MDL).
Discussion: Overall, when tuned for optimal selection of thresholds, our method offers researchers a precise tool to estimate the true number of active brain sources and accurately model brain function.
Keywords: AIC; Alternating Projection (AP); F-ratio; MDL; MEG; source enumeration; source localization.
Copyright © 2023 Giri, Mosher, Adler and Pantazis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Modified covariance beamformer for solving MEG inverse problem in the environment with correlated sources.Neuroimage. 2021 Mar;228:117677. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117677. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Neuroimage. 2021. PMID: 33385549
-
Localization of Brain Signals by Alternating Projection.Biomed Signal Process Control. 2024 Apr;90:105796. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2023.105796. Epub 2023 Dec 9. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2024. PMID: 38249934 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of MEG source reconstruction method on source-space connectivity estimation: A comparison between minimum-norm solution and beamforming.Neuroimage. 2017 Aug 1;156:29-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.04.038. Epub 2017 May 4. Neuroimage. 2017. PMID: 28479475
-
MEG and EEG in epilepsy.J Clin Neurophysiol. 2003 May-Jun;20(3):163-78. doi: 10.1097/00004691-200305000-00002. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2003. PMID: 12881663 Review.
-
Combining MEG and EEG source modeling in epilepsy evaluations.J Clin Neurophysiol. 2010 Dec;27(6):360-71. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0b013e318201ffc4. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 21076318 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation and Characterization of High-Uniformity SiNx Thin Film with Controllable Refractive Index by Home-Made Cat-CVD Based on Orthogonal Experiments.Molecules. 2025 Feb 27;30(5):1091. doi: 10.3390/molecules30051091. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40076315 Free PMC article.
-
LOCALIZATION OF SPATIALLY EXTENDED BRAIN SOURCES BY FLEXIBLE ALTERNATING PROJECTION (FLEX-AP).bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 8:2023.11.03.565461. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.03.565461. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2025 Apr;72(4):1486-1497. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2024.3509741. PMID: 37961131 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Flexible Alternating Projection for Spatially Extended Brain Source Localization.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2025 Apr;72(4):1486-1497. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2024.3509741. Epub 2025 Mar 21. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2025. PMID: 40030749
References
-
- Adler A., Wax M., Pantazis D. (2022). “Brain source localization by alternating projection,” in 2022 IEEE 19th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), (IEEE), p. 1–5.
-
- Akaike H. (1974). A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 19, 716–723. 10.1109/TAC.1974.1100705 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

