Unusual paranasal sinus solitary neurofibroma and literature review
- PMID: 37780973
- PMCID: PMC10513009
- DOI: 10.1259/bjrcr.20230025
Unusual paranasal sinus solitary neurofibroma and literature review
Abstract
Neurofibroma (NF) is a common benign peripheral neurogenic tumor that is rarely encountered in the paranasal sinus tract. In this report, we present a 55-year-old female who serendipitously discovered a maxillary sinus NF during a medical examination for a pulmonary nodule. The purpose of this article is to enhance medical practitioners' comprehension of paranasal sinus solitary NF by exploring cases, summarizing occurrences located in the paranasal sinus tract and conducting an organized review of paranasal sinus tract NF.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by the British Institute of Radiology.
Figures
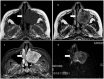
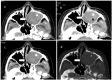
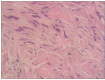
Similar articles
-
Solitary neurofibroma of the frontal sinus.Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2012;2012:373808. doi: 10.1155/2012/373808. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2012. PMID: 22928136 Free PMC article.
-
A rare solitary neurofibroma of the frontal sinus.J Craniofac Surg. 2014 Jul;25(4):1542-4. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000000784. J Craniofac Surg. 2014. PMID: 24914758
-
[Solitary neurofibroma of the maxillary sinus].Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac. 2009 Nov-Dec;126(5-6):256-8. doi: 10.1016/j.aorl.2009.10.001. Epub 2009 Nov 14. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac. 2009. PMID: 19914596 French.
-
Peripheral nerve tumors involving paranasal sinuses: a case report and review of the literature.Cancer. 1975 Apr;35(4):1254-8. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197504)35:4<1254::aid-cncr2820350433>3.0.co;2-3. Cancer. 1975. PMID: 803868 Review.
-
[Metastases to the paranasal sinuses: case report and review of the literature].Laryngorhinootologie. 2001 Oct;80(10):583-94. doi: 10.1055/s-2001-17835. Laryngorhinootologie. 2001. PMID: 11602931 Review. German.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

