Polysaccharides: potential bioactive macromolecules for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 37781122
- PMCID: PMC10540640
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1249018
Polysaccharides: potential bioactive macromolecules for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
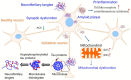
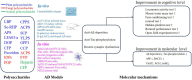
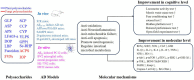
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is one of the leading causes of death and disability. AD is a devastating disease that has caused an overwhelming burden. However, no disease-modified treatment was discovered. The approval of sodium oligomannate (GV-971) in mild-moderate AD patients has attracted great attention to investigate the role of saccharides in AD. Therefore, summarizing and explaining the role of saccharides in AD is urgent and promising. Recent studies showed that polysaccharides (PSs) potentially benefit AD in vitro and in vivo. PSs could alleviate the pathological damage and improve cognitive symptoms via (1) antagonizing the toxicity of abnormal amyloid-beta and tau proteins; (2) attenuating oxidative stress and proinflammation; (3) rebuilding neuroplasticity. PSs exhibit one-multiple pathological hits of AD. However, a thorough chemical investigation is needed for further study.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid-beta; inflammation; oxidative stress; polysaccharide.
Copyright © 2023 Peng, Li and Meng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Servick K ND. Alzheimer’s experts greet China’s surprise approval of a drug for brain disease with Hope and caution. Asia Pacific Health science mag org, (2019)
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

