Baricitinib protects mice from sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction and multiple-organ failure
- PMID: 37781388
- PMCID: PMC10536262
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1223014
Baricitinib protects mice from sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction and multiple-organ failure
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Baricitinib protects mice from sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction and multiple-organ failure.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 8;15:1521254. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1521254. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39582858 Free PMC article.
Abstract
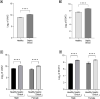
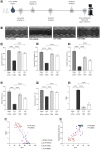
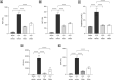
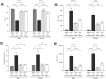
Sepsis is one of the major complications of surgery resulting in high morbidity and mortality, but there are no specific therapies for sepsis-induced organ dysfunction. Data obtained under Gene Expression Omnibus accession GSE131761 were re-analyzed and showed an increased gene expression of Janus Kinase 2 (JAK2) and Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) in the whole blood of post-operative septic patients. Based on these results, we hypothesized that JAK/STAT activation may contribute to the pathophysiology of septic shock and, hence, investigated the effects of baricitinib (JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor) on sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction and multiple-organ failure (MOF). In a mouse model of post-trauma sepsis induced by midline laparotomy and cecal ligation and puncture (CLP), 10-week-old male (n=32) and female (n=32) C57BL/6 mice received baricitinib (1mg/kg; i.p.) or vehicle at 1h or 3h post-surgery. Cardiac function was assessed at 24h post-CLP by echocardiography in vivo, and the degree of MOF was analyzed by determination of biomarkers in the serum. The potential mechanism underlying both the cardiac dysfunction and the effect of baricitinib was analyzed by western blot analysis in the heart. Trauma and subsequent sepsis significantly depressed the cardiac function and induced multiple-organ failure, associated with an increase in the activation of JAK2/STAT3, NLRP3 inflammasome and NF- κβ pathways in the heart of both male and female animals. These pathways were inhibited by the administration of baricitinib post the onset of sepsis. Moreover, treatment with baricitinib at 1h or 3h post-CLP protected mice from sepsis-induced cardiac injury and multiple-organ failure. Thus, baricitinib may be repurposed for trauma-associated sepsis.
Keywords: Janus Kinase; baricitinib; cardiac dysfunction; multiple-organ failure; sepsis.
Copyright © 2023 Verra, Mohammad, Alves, Porchietto, Coldewey, Collino and Thiemermann.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spleen tyrosine kinase: a novel pharmacological target for sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction and multi-organ failure.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 4;15:1447901. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1447901. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39559354 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the JAK/STAT Pathway With Baricitinib Reduces the Multiple Organ Dysfunction Caused by Hemorrhagic Shock in Rats.Ann Surg. 2023 Jul 1;278(1):e137-e146. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000005571. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Ann Surg. 2023. PMID: 35837955 Free PMC article.
-
Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition Attenuates the Cardiac Dysfunction Caused by Cecal Ligation and Puncture in Mice.Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 6;10:2129. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02129. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. Retraction in: Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 27;16:1561869. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1561869. PMID: 31552054 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Inhibition of Janus kinase 2 and signal transduction and activator of transcription 3 protect against cecal ligation and puncture-induced multiple organ damage and mortality.J Trauma. 2009 Mar;66(3):859-65. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e318164d05f. J Trauma. 2009. PMID: 19276765
-
JAK2 inhibitor protects the septic heart through enhancing mitophagy in cardiomyocytes.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Sep;178:117279. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117279. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39121587
Cited by
-
Spleen tyrosine kinase: a novel pharmacological target for sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction and multi-organ failure.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 4;15:1447901. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1447901. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39559354 Free PMC article.
-
NLRP3 Inflammasome Targeting Offers a Novel Therapeutic Paradigm for Sepsis-Induced Myocardial Injury.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Feb 14;19:1025-1041. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S506537. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 39967903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From immune dysregulation to organ dysfunction: understanding the enigma of Sepsis.Front Microbiol. 2024 Aug 26;15:1415274. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1415274. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39252831 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, et al. . Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet (London England) (2020) 395(10219):200–11. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

