SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination induces an intranasal mucosal response characterized by neutralizing antibodies
- PMID: 37781659
- PMCID: PMC10290737
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacig.2023.100129
SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination induces an intranasal mucosal response characterized by neutralizing antibodies
Abstract
Background: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) mRNA vaccine-induced systemic antibody profiles are well characterized; however, little is known about whether intranasal mucosal antibodies are induced or can neutralize virus in response to mRNA vaccination.
Objective: We sought to evaluate intranasal mucosal antibody production with SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination.
Methods: SARS-CoV-2-specific IgG and IgA concentrations and neutralization activity from sera and nasal mucosa via nasal epithelial lining fluid (NELF) collection were measured in SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-vaccinated healthy volunteers (N = 29) by using multiplex immunoassays. Data were compared before and after vaccination, between mRNA vaccine brands, and by sex.
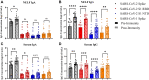
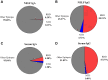
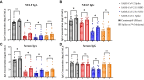
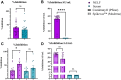
Results: SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination induced an intranasal immune response characterized by neutralizing mucosal antibodies. IgG antibodies displayed greater Spike 1 (S1) binding specificity than did IgA in serum and nasal mucosa. Nasal antibodies displayed greater neutralization activity against the receptor-binding domain than serum. Spikevax (Moderna)-vaccinated individuals displayed greater SARS-CoV-2-specific IgG and IgA antibody concentrations than did Comirnaty (BioNTech/Pfizer)-vaccinated individuals in their serum and nasal epithelial lining fluid. Sex-dependent differences in antibody response were not observed.
Conclusion: SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination induces a robust systemic and intranasal antibody production with neutralizing capacity. Spikevax vaccinations elicit a greater antibody response than does Comirnaty vaccination systemically and intranasally.
Keywords: NELF; SARS-CoV-2; antibodies; antigens; epitope; mRNA vaccine; mucosal immune response; neutralization; serum; systemic immune response.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Mucosal and Serological Immune Responses to the Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Vaccines.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 12;12:744887. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.744887. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34712232 Free PMC article.
-
A Single Dose of BNT162b2 Messenger RNA Vaccine Induces Airway Immunity in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Naive and Recovered Coronavirus Disease 2019 Subjects.Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Dec 19;75(12):2053-2059. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciac378. Clin Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35579991 Free PMC article.
-
An Intranasal OMV-Based Vaccine Induces High Mucosal and Systemic Protecting Immunity Against a SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 17;12:781280. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.781280. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34987509 Free PMC article.
-
Saliva is suitable for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies detection after vaccination: A rapid systematic review.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 20;13:1006040. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1006040. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36203571 Free PMC article.
-
Review: The Nose as a Route for Therapy. Part 2 Immunotherapy.Front Allergy. 2021 Jul 1;2:668781. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2021.668781. eCollection 2021. Front Allergy. 2021. PMID: 35387044 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Serum and Salivary IgG and IgA Response After COVID-19 Messenger RNA Vaccination.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Apr 1;7(4):e248051. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.8051. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38652471 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Novel Nasal Mucoadhesive Nanoformulations Containing Lipid-Soluble EGCG for Long COVID Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jun 11;16(6):791. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16060791. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38931912 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 mRNA vaccines are effective at stopping a nosy virus.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025 Jan 30;36(1):102458. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102458. eCollection 2025 Mar 11. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025. PMID: 39967854 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Passive infusion of an S2-Stem broadly neutralizing antibody protects against SARS-CoV-2 infection and lower airway inflammation in rhesus macaques.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Jan 23;21(1):e1012456. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012456. eCollection 2025 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 39847599 Free PMC article.
-
Use of a point-of-care test to rapidly assess levels of SARS-CoV-2 nasal neutralising antibodies in vaccines and breakthrough infected individuals.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 20;13(1):20263. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47613-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37985674 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Janeway C., editor. Immunobiology: the immune system in health and disease [animated CD-ROM inside] 5th ed. Garland Publishing; New York, NY: 2001. p. 732.
-
- Ainai A., Suzuki T., Tamura S.I., Hasegawa H. intranasal administration of whole inactivated influenza virus vaccine as a promising influenza vaccine candidate. Viral Immunol. 2017;30:451–462. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

