Effectiveness and safety of oral anticoagulants for non-valvular atrial fibrillation: a population-based cohort study in primary healthcare in Catalonia
- PMID: 37781690
- PMCID: PMC10540223
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1237454
Effectiveness and safety of oral anticoagulants for non-valvular atrial fibrillation: a population-based cohort study in primary healthcare in Catalonia
Abstract
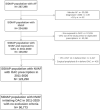
Objectives: Our objective was to analyse effectiveness and safety of oral anticoagulants (OAC) for stroke prevention in non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Material and methods: Population-based cohort study including adults initiating oral anticoagulants, either direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) or vitamin K antagonists (VKA), during 2011-2020. Data source: SIDIAP, capturing information from the electronic health records of Primary Health Care in Catalonia, Spain. Study outcomes: stroke, cerebral and gastrointestinal (GI) haemorrhage, assessed by patients' subgroups according to different clinical characteristics. Results: We included 90,773 patients. Male sex, older than 75, previous event, peripheral artery disease, deep vein thrombosis, or receiving antiplatelets, antidiabetics or proton pump inhibitors (PPI) was associated with higher stroke risk. For DOAC-treated, treatment switch increased stroke risk, while being adherent had a protective effect. Men, antidiabetic treatment or a previous event increased the risk of cerebral bleeding. Receiving direct oral anticoagulants had a protective effect in comparison to vitamin K antagonists. For DOAC-treated, treatment switch increased, and adherence decreased the bleeding risk. Men, people with chronic kidney disease or a previous event posed an increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, whereas receiving PPI had a protective effect. For DOAC-treated, switch was associated with a higher bleeding risk. Conclusion: Being men, a previous event and DOAC-switch posed a higher risk for all study outcomes. direct oral anticoagulants had a protective effect against cerebral bleeding in comparison to vitamin K antagonists. Adherence to direct oral anticoagulants resulted in lower risk of stroke and cerebral bleeding. We found no differences in the risk of stroke and gastrointestinal bleeding when we compared direct oral anticoagulants vs. vitamin K antagonists.
Keywords: adherence; atrial fibrillation; effectiveness; electronic health records; oral anticoagulants; primary healthcare; safety; stroke.
Copyright © 2023 Giner-Soriano, Ouchi, Vives, Vilaplana-Carnerero, Molina, Vallano and Morros.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ahn H. J., Lee S. R., Choi E. K., Rhee T. M., Kwon S., Oh S., et al. (2022). Protective effect of proton-pump inhibitor against gastrointestinal bleeding in patients receiving oral anticoagulants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 88, 4676–4687. 10.1111/BCP.15478 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anguita Sánchez M., Bertomeu Martínez V., Ruiz Ortiz M., Cequier Fillat Á., Roldán Rabadán I., Muñiz García J., et al. (2020). Direct oral anticoagulants versus vitamin K antagonists in real-world patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. The FANTASIIA study. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 73, 14–20. 10.1016/j.rec.2019.02.021 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bang O. Y., On Y. K., Lee M. Y., Jang S. W., Han S., Han S., et al. (2020). The risk of stroke/systemic embolism and major bleeding in Asian patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation treated with non-vitamin K oral anticoagulants compared to warfarin: Results from a real-world data analysis. PLoS One 15, e0242922. 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0242922 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

