Identification of novel lactate metabolism-related lncRNAs with prognostic value for bladder cancer
- PMID: 37781694
- PMCID: PMC10533998
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1215296
Identification of novel lactate metabolism-related lncRNAs with prognostic value for bladder cancer
Abstract
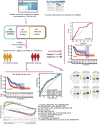
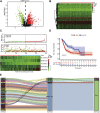
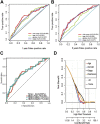
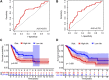
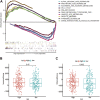
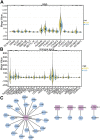
Background: Bladder cancer (BCA) has high recurrence and metastasis rates, and current treatment options show limited efficacy and significant adverse effects. It is crucial to find diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets with clinical value. This study aimed to identify lactate metabolism-related lncRNAs (LM_lncRNAs) to establish a model for evaluating bladder cancer prognosis. Method: A risk model consisting of lactate metabolism-related lncRNAs was developed to forecast bladder cancer patient prognosis using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Kaplan‒Meier survival analysis, receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis and decision curve analysis (DCA) were used to evaluate the reliability of risk grouping for predictive analysis of bladder cancer patients. The results were also validated in the validation set. Chemotherapeutic agents sensitive to lactate metabolism were assessed using the Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer (GDSC) database. Results: As an independent prognostic factor for patients, lactate metabolism-related lncRNAs can be used as a nomogram chart that predicts overall survival time (OS). There were significant differences in survival rates between the high-risk and low-risk groups based on the Kaplan‒Meier survival curve. decision curve analysis and receiver operating characteristic curve analysis confirmed its good predictive capacity. As a result, 22 chemotherapeutic agents were predicted to positively affect the high-risk group. Conclusion: An lactate metabolism-related lncRNA prediction model was proposed to predict the prognosis for patients with bladder cancer and chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in high-risk groups, which provided a new idea for the prognostic evaluation of the clinical treatment of bladder cancer.
Keywords: bladder cancer; lactate metabolism; lncRNAs; molecular subtype; prognostic model.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Pan, Guan, Ren, Wang, Wei and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of a Novel Glycolysis-Related LncRNA Signature for Predicting Overall Survival in Patients With Bladder Cancer.Front Genet. 2021 Aug 19;12:720421. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.720421. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34490046 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel lactate metabolism signatures and molecular subtypes for prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 2;10:960277. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.960277. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36147735 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel defined inflammation-related long noncoding RNA signature contributes to predicting prognosis and distinction between the cold and hot tumors in bladder cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 29;13:972558. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.972558. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37064115 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a prognostic model of colon cancer patients based on metabolism-related lncRNAs.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 29;12:944476. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.944476. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36248984 Free PMC article.
-
A robust signature of immune-related long non-coding RNA to predict the prognosis of bladder cancer.Cancer Med. 2021 Sep;10(18):6534-6545. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4167. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34374227 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bollard J., Miguela V., Ruiz de Galarreta M., Venkatesh A., Bian C. B., Roberto M. P., et al. (2017). Palbociclib (PD-0332991), a selective CDK4/6 inhibitor, restricts tumour growth in preclinical models of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 66 (7), 1286–1296. 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312268 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown T. P., Bhattacharjee P., Ramachandran S., Sivaprakasam S., Ristic B., Sikder M. O. F., et al. (2020). The lactate receptor GPR81 promotes breast cancer growth via a paracrine mechanism involving antigen-presenting cells in the tumor microenvironment. Oncogene 39 (16), 3292–3304. 10.1038/s41388-020-1216-5 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

