Recent advances in the study of anesthesia-and analgesia-related mechanisms of S-ketamine
- PMID: 37781698
- PMCID: PMC10539608
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1228895
Recent advances in the study of anesthesia-and analgesia-related mechanisms of S-ketamine
Abstract
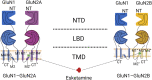
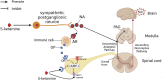
Ketamine is a racemic mixture of equal amounts of R-ketamine and S-ketamine and is well known to anesthesiologists for its unique dissociative anesthetic properties. The pharmacological properties of ketamine, namely, its sympathetic excitation, mild respiratory depression, and potent analgesia, are still highly valued in its use as an anesthetic for some patients. In particular, since its advent, S-ketamine has been widely used as an anesthetic in many countries due to its increased affinity for NMDA receptors and its enhanced anesthetic and analgesic effects. However, the anesthetic and analgesic mechanisms of S-ketamine are not fully understood. In addition to antagonizing NMDA receptors, a variety of other receptors or channels may be involved, but there are no relevant mechanistic summaries in the literature. Therefore, the purpose of this paper is to review the mechanisms of action of S-ketamine on relevant receptors and systems in the body that result in its pharmacological properties, such as anesthesia and analgesia, with the aim of providing a reference for its clinical applications and research.
Keywords: AMPA; NMDA; S-ketamine; analgesia; anesthesia; ketamine; opioid receptor.
Copyright © 2023 Zhou, Peng, Liang, Chen, Liu, Wang, Guo, Deng, Ye, Zhong and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bieber M., Schwerin S., Kreuzer M., Klug C., Henzler M., Schneider G., et al. (2022). s-ketamine enhances thalamocortical and corticocortical synaptic transmission in acute murine brain slices via increased AMPA-receptor-mediated pathways. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 16, 1044536. 10.3389/fnsys.2022.1044536 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bornemann-Cimenti H., Wejbora M., Michaeli K., Edler A., Sandner-Kiesling A. (2016). The effects of minimal-dose versus low-dose S-ketamine on opioid consumption, hyperalgesia, and postoperative delirium: A triple-blinded, randomized, active- and placebo-controlled clinical trial. Minerva Anestesiol. 82 (10), 1069–1076. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

