The effect of Shengmai injection in patients with coronary heart disease in real world and its personalized medicine research using machine learning techniques
- PMID: 37781710
- PMCID: PMC10537936
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1208621
The effect of Shengmai injection in patients with coronary heart disease in real world and its personalized medicine research using machine learning techniques
Abstract
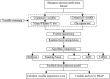
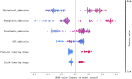
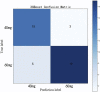
Objective: Shengmai injection is a common treatment for coronary heart disease. The accurate dose regimen is important to maximize effectiveness and minimize adverse reactions. We aim to explore the effect of Shengmai injection in patients with coronary heart disease based on real-world data and establish a personalized medicine model using machine learning and deep learning techniques. Methods: 211 patients were enrolled. The length of hospital stay was used to explore the effect of Shengmai injection in a case-control study. We applied propensity score matching to reduce bias and Wilcoxon rank sum test to compare results between the experimental group and the control group. Important variables influencing the dose regimen of Shengmai injection were screened by XGBoost. A personalized medicine model of Shengmai injection was established by XGBoost selected from nine algorithm models. SHapley Additive exPlanations and confusion matrix were used to interpret the results clinically. Results: Patients using Shengmai injection had shorter length of hospital stay than those not using Shengmai injection (median 10.00 days vs. 11.00 days, p = 0.006). The personalized medicine model established via XGBoost shows accuracy = 0.81 and AUC = 0.87 in test cohort and accuracy = 0.84 and AUC = 0.84 in external verification. The important variables influencing the dose regimen of Shengmai injection include lipid-lowering drugs, platelet-lowering drugs, levels of GGT, hemoglobin, prealbumin, and cholesterol at admission. Finally, the personalized model shows precision = 75%, recall rate = 83% and F1-score = 79% for predicting 40 mg of Shengmai injection; and precision = 86%, recall rate = 79% and F1-score = 83% for predicting 60 mg of Shengmai injection. Conclusion: This study provides evidence supporting the clinical effectiveness of Shengmai injection, and established its personalized medicine model, which may help clinicians make better decisions.
Keywords: Shengmai; coronary heart disease; machine learning; personalized medicine; real world.
Copyright © 2023 Ma, Yu, Chen, Li, Liu, Chen, Lyu, Hao, Zhang, Wang, Gao, Zhang and Bu.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors XH and SW were employed by Dalian Medicinovo Technology Co., Ltd. and Authors JYZ and FG were employed by Beijing Medicinovo Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Predicting Lapatinib Dose Regimen Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques Based on a Real-World Study.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 3;12:893966. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.893966. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35719963 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Four Machine Learning Techniques for Prediction of Intensive Care Unit Length of Stay in Heart Transplantation Patients.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jun 21;9:863642. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.863642. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35800164 Free PMC article.
-
An individualized medication model of sodium valproate for patients with bipolar disorder based on machine learning and deep learning techniques.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 17;13:890221. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.890221. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36339624 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Arteriosclerotic Heart Disease Patients Using Electronic Health Records: A Machine Learning and Shapley Additive exPlanations Approach.Healthc Inform Res. 2023 Jul;29(3):228-238. doi: 10.4258/hir.2023.29.3.228. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Healthc Inform Res. 2023. PMID: 37591678 Free PMC article.
-
Shengmai injection as an adjunctive therapy for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Complement Ther Med. 2019 Apr;43:140-147. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2019.01.020. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Complement Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 30935521
Cited by
-
Explainable Artificial Intelligence in the Field of Drug Research.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 May 29;19:4501-4516. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S525171. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40458811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Different Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Agonists on IVF/ICSI-ET Outcomes in Long Protocol: A Retrospective Study.Int J Womens Health. 2025 May 8;17:1313-1320. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S517738. eCollection 2025. Int J Womens Health. 2025. PMID: 40357020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aksakal E., Tanboga I. H., Kurt M., Kaygın M. A., Kaya A., Isik T., et al. (2012). The relation of serum gamma-glutamyl transferase levels with coronary lesion complexity and long-term outcome in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 221 (2), 596–601. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.01.044 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arik S. O., Pfister T. (2019). TabNet: Attentive interpretable tabular learning. arXiv.
-
- Branch K. R., Probstfield J. L., Eikelboom J. W., Bosch J., Maggioni A. P., Cheng R. K., et al. (2019). Rivaroxaban with or without aspirin in patients with heart failure and chronic coronary or peripheral artery disease. Circulation 140 (7), 529–537. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.039609 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

