Biocatalysis in Drug Design: Engineered Reductive Aminases (RedAms) Are Used to Access Chiral Building Blocks with Multiple Stereocenters
- PMID: 37782882
- PMCID: PMC10571080
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c07010
Biocatalysis in Drug Design: Engineered Reductive Aminases (RedAms) Are Used to Access Chiral Building Blocks with Multiple Stereocenters
Abstract
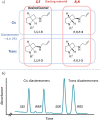
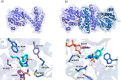
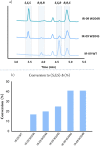
Novel building blocks are in constant demand during the search for innovative bioactive small molecule therapeutics by enabling the construction of structure-activity-property-toxicology relationships. Complex chiral molecules containing multiple stereocenters are an important component in compound library expansion but can be difficult to access by traditional organic synthesis. Herein, we report a biocatalytic process to access a specific diastereomer of a chiral amine building block used in drug discovery. A reductive aminase (RedAm) was engineered following a structure-guided mutagenesis strategy to produce the desired isomer. The engineered RedAm (IR-09 W204R) was able to generate the (S,S,S)-isomer 3 in 45% conversion and 95% ee from the racemic ketone 2. Subsequent palladium-catalyzed deallylation of 3 yielded the target primary amine 4 in a 73% yield. This engineered biocatalyst was used at preparative scale and represents a potential starting point for further engineering and process development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chen K.; Arnold F. H. Engineering New Catalytic Activities in Enzymes. Nature Catalysis 2020, 203–213. 10.1038/s41929-019-0385-5. - DOI
-
- Thorpe T. W.; Marshall J. R.; Harawa V.; Ruscoe R. E.; Cuetos A.; Finnigan J. D.; Angelastro A.; Heath R. S.; Parmeggiani F.; Charnock S. J.; Howard R. M.; Kumar R.; Daniels D. S. B.; Grogan G.; Turner N. J. Multifunctional Biocatalyst for Conjugate Reduction and Reductive Amination. Nature 2022, 604 (7904), 86–91. 10.1038/s41586-022-04458-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kumar R.; Karmilowicz M. J.; Burke D.; Burns M. P.; Clark L. A.; Connor C. G.; Cordi E.; Do N. M.; Doyle K. M.; Hoagland S.; Lewis C. A.; Mangan D.; Martinez C. A.; McInturff E. L.; Meldrum K.; Pearson R.; Steflik J.; Rane A.; Weaver J. Biocatalytic Reductive Amination from Discovery to Commercial Manufacturing Applied to Abrocitinib JAK1 Inhibitor. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4 (9), 775–782. 10.1038/s41929-021-00671-5. - DOI
-
- Schober M.; MacDermaid C.; Ollis A. A.; Chang S.; Khan D.; Hosford J.; Latham J.; Ihnken L. A. F.; Brown M. J. B.; Fuerst D.; Sanganee M. J.; Roiban G. D. Chiral Synthesis of LSD1 Inhibitor GSK2879552 Enabled by Directed Evolution of an Imine Reductase. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2 (10), 909–915. 10.1038/s41929-019-0341-4. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

