Streamlined and sensitive mono- and di-ribosome profiling in yeast and human cells
- PMID: 37783882
- PMCID: PMC11276118
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-023-02028-1
Streamlined and sensitive mono- and di-ribosome profiling in yeast and human cells
Abstract
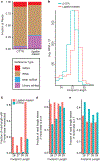
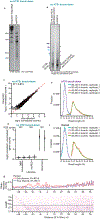
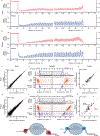
Ribosome profiling has unveiled diverse regulation and perturbations of translation through a transcriptome-wide survey of ribosome occupancy, read out by sequencing of ribosome-protected messenger RNA fragments. Generation of ribosome footprints and their conversion into sequencing libraries is technically demanding and sensitive to biases that distort the representation of physiological ribosome occupancy. We address these challenges by producing ribosome footprints with P1 nuclease rather than RNase I and replacing RNA ligation with ordered two-template relay, a single-tube protocol for sequencing library preparation that incorporates adaptors by reverse transcription. Our streamlined approach reduced sequence bias and enhanced enrichment of ribosome footprints relative to ribosomal RNA. Furthermore, P1 nuclease preserved distinct juxtaposed ribosome complexes informative about yeast and human ribosome fates during translation initiation, stalling and termination. Our optimized methods for mRNA footprint generation and capture provide a richer translatome profile with low input and fewer technical challenges.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
L.F, H.E.U., S.C.P, and K.C. are named inventors on patent applications filed by the University of California describing biochemical activities of RTs used for OTTR. H.E.U. and K.C. have equity in Karnateq, Inc., which licensed the technology and is producing kits for OTTR cDNA library preparation. N.T.I. declares equity in Tevard Biosciences and Velia Therapeutics.
Figures














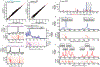
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

