A subpopulation of lipogenic brown adipocytes drives thermogenic memory
- PMID: 37783943
- PMCID: PMC11309804
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-023-00893-w
A subpopulation of lipogenic brown adipocytes drives thermogenic memory
Abstract
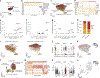
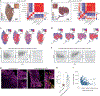
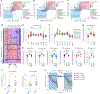
Sustained responses to transient environmental stimuli are important for survival. The mechanisms underlying long-term adaptations to temporary shifts in abiotic factors remain incompletely understood. Here, we find that transient cold exposure leads to sustained transcriptional and metabolic adaptations in brown adipose tissue, which improve thermogenic responses to secondary cold encounter. Primary thermogenic challenge triggers the delayed induction of a lipid biosynthesis programme even after cessation of the original stimulus, which protects from subsequent exposures. Single-nucleus RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics reveal that this response is driven by a lipogenic subpopulation of brown adipocytes localized along the perimeter of Ucp1hi adipocytes. This lipogenic programme is associated with the production of acylcarnitines, and supplementation of acylcarnitines is sufficient to recapitulate improved secondary cold responses. Overall, our data highlight the importance of heterogenous brown adipocyte populations for 'thermogenic memory', which may have therapeutic implications for leveraging short-term thermogenesis to counteract obesity.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
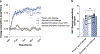



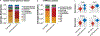


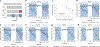


References
-
- Farber DL, Netea MG, Radbruch A, Rajewsky K & Zinkernagel RM Immunological memory: lessons from the past and a look to the future. Nat. Rev. Immunol 16, 124–128 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Josselyn SA, Köhler S & Frankland PW Finding the engram. Nat. Rev. Neurosci 16, 521–534 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Kandel ER, Dudai Y & Mayford MR The molecular and systems biology of memory. Cell 157, 163–186 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

