Enteral citrulline supplementation versus placebo on SOFA score on day 7 in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients: the IMMUNOCITRE randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 37784110
- PMCID: PMC10546668
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-023-04651-y
Enteral citrulline supplementation versus placebo on SOFA score on day 7 in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients: the IMMUNOCITRE randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Restoring plasma arginine levels through enteral administration of L-citrulline in critically ill patients may improve outcomes. We aimed to evaluate whether enteral L-citrulline administration reduced organ dysfunction based on the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score and affected selected immune parameters in mechanically ventilated medical intensive care unit (ICU) patients.
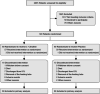
Methods: A randomized, double-blind, multicenter clinical trial of enteral administration of L-citrulline versus placebo for critically ill adult patients under invasive mechanical ventilation without sepsis or septic shock was conducted in four ICUs in France between September 2016 and February 2019. Patients were randomly assigned to receive enteral L-citrulline (5 g) every 12 h for 5 days or isonitrogenous, isocaloric placebo. The primary outcome was the SOFA score on day 7. Secondary outcomes included SOFA score improvement (defined as a decrease in total SOFA score by 2 points or more between day 1 and day 7), secondary infection acquisition, ICU length of stay, plasma amino acid levels, and immune biomarkers on day 3 and day 7 (HLA-DR expression on monocytes and interleukin-6).
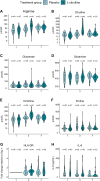
Results: Of 120 randomized patients (mean age, 60 ± 17 years; 44 [36.7%] women; ICU stay 10 days [IQR, 7-16]; incidence of secondary infections 25 patients (20.8%)), 60 were allocated to L-citrulline and 60 were allocated to placebo. Overall, there was no significant difference in organ dysfunction as assessed by the SOFA score on day 7 after enrollment (4 [IQR, 2-6] in the L-citrulline group vs. 4 [IQR, 2-7] in the placebo group; Mann‒Whitney U test, p = 0.9). Plasma arginine was significantly increased on day 3 in the treatment group, while immune parameters remained unaffected.
Conclusion: Among mechanically ventilated ICU patients without sepsis or septic shock, enteral L-citrulline administration did not result in a significant difference in SOFA score on day 7 compared to placebo.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT02864017 (date of registration: 11 August 2016).
Keywords: Critical care; Immunonutrition; Plasma arginine; Plasma citrulline; SOFA score.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Jean-Marc Tadié received personal fees from Biomerieux; Nicolas Terzi received personal fees from Pfizer; Jean-Luc Diehl reports research supports, grants and personal fees from ALung Technologies, Xenios, Fresenius Medical Care and Baxter, RonanThibault reports Royalties for designing the Simple Evaluation of Food Intake® (SEFI®) (Knoë, le Kremlin Bicêtre, France), consulting fees from Nestlé Health Science, Servier, Baxter, BBraun, Fresenius-Kabi, Nutricia, LeCancer and Nutricia, NHC, Novonordisk; Luc Cynober is a shareholder of Citrage Co, member of the Citrage Co Scientific Committee.
Figures

References
-
- Davis JS, Anstey NM. Is plasma arginine concentration decreased in patients with sepsis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care Med. 2011;39(2):380–385. - PubMed
-
- Zhou M, Martindale RG. Arginine in the critical care setting. J Nutr. 2007;137(6 Suppl 2):1687S–S1692. - PubMed
-
- Bronte V, Zanovello P. Regulation of immune responses by L-arginine metabolism. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5(8):641–654. - PubMed
-
- Arginine metabolism: enzymology, nutrition, and clinical significance. In: Proceedings of a symposium dedicated to the memory of Vernon R. Young. April 5–6, 2004. Bermuda. The Journal of nutrition. 2004;134(10 Suppl):2741S–897S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

