A typically progressive dissection of the internal carotid artery with recurrent hiccups: A case report with continuous 2-year data recording
- PMID: 37786522
- PMCID: PMC10529161
- DOI: 10.1002/ibra.12074
A typically progressive dissection of the internal carotid artery with recurrent hiccups: A case report with continuous 2-year data recording
Abstract
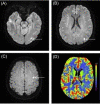
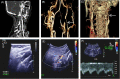
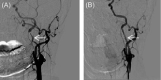
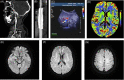
Patients with internal carotid artery dissection (ICAD) usually report headache, neck pain, Horner's syndrome, and ischemic stroke. Because the posterior cranial nerve is involved, some patients may show different forms of posterior cranial nerve paralysis. There have been no reports of patients with ICAD showing repeated hiccups. Here, to help clinicians identify ICAD early and gain a better understanding of the atypical manifestations of the disease, we report an atypical case of recurrent hiccup symptoms caused by ICAD.
Keywords: digital subtraction angiography (DSA); internal carotid artery dissection (ICAD); magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); recurrent hiccups.
© 2022 The Authors. Ibrain published by Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University (AHZMU) and Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
