Breakthroughs on the clinical management of headache and questions that need to be solved
- PMID: 37786564
- PMCID: PMC10529177
- DOI: 10.1002/ibra.12003
Breakthroughs on the clinical management of headache and questions that need to be solved
Abstract
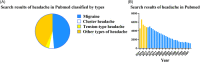
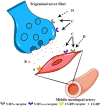
Headache is a common refractory disorder among adults, especially in females, which can lower the quality of life in patients and increase medical costs. Nearly 90% of people have been affected by headache disorders during their lifetime. The severe situation of headaches has drawn the attention of researchers in recent years. Although the mechanism of headache has not been fully understood by us, there are many effective preventive drugs and treatments available. This review is aimed to sum up the progress in clinical trials of headaches in the past 5 years.
Keywords: clinical trial; headache; mechanism; prevention; therapeutics.
© 2021 The Authors. Ibrain published by Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University and Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neuroimaging for the evaluation of chronic headaches: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010;10(26):1-57. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010. PMID: 23074404 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and Management of Headache: A Review.JAMA. 2021 May 11;325(18):1874-1885. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.1640. JAMA. 2021. PMID: 33974014 Review.
-
Trial protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial to assess the efficacy and safety of intravenous ketamine for chronic daily headaches: the "KetHead" trial.Trials. 2023 Mar 1;24(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07186-3. Trials. 2023. PMID: 36855160 Free PMC article.
-
"It's just part of who I am…" Living with chronic headache: voices from the CHESS trial, a qualitative study.BMC Neurol. 2024 Aug 2;24(1):268. doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-03779-w. BMC Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39095730 Free PMC article.
-
Headache in Children and Adolescents.Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2021 Jun 1;27(3):703-731. doi: 10.1212/CON.0000000000000993. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2021. PMID: 34048400 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stellate ganglion intervention for chronic pain: A review.Ibrain. 2022 May 28;8(2):210-218. doi: 10.1002/ibra.12047. eCollection 2022 Summer. Ibrain. 2022. PMID: 37786891 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pezzini A, Busto G, Zedde M, et al. Vulnerability to infarction during cerebral ischemia in migraine sufferers. Stroke. 2018;49(3):573‐578. - PubMed
-
- Robbins MS. Diagnosis and management of headache: a review. JAMA. 2021;325(18):1874‐1885. - PubMed
-
- Goadsby PJ. Headache research in 2020: disrupting and improving practice. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20(1):7‐8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
