Inactivation of TRPM7 Kinase Targets AKT Signaling and Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Human CML Cells
- PMID: 37786778
- PMCID: PMC10541797
- DOI: 10.1093/function/zqad053
Inactivation of TRPM7 Kinase Targets AKT Signaling and Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Human CML Cells
Abstract
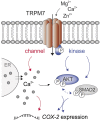
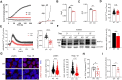
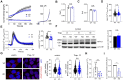
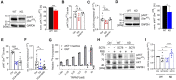
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is a key regulator of inflammation. High constitutive COX-2 expression enhances survival and proliferation of cancer cells, and adversely impacts antitumor immunity. The expression of COX-2 is modulated by various signaling pathways. Recently, we identified the melastatin-like transient-receptor-potential-7 (TRPM7) channel-kinase as modulator of immune homeostasis. TRPM7 protein is essential for leukocyte proliferation and differentiation, and upregulated in several cancers. It comprises of a cation channel and an atypical α-kinase, linked to inflammatory cell signals and associated with hallmarks of tumor progression. A role in leukemia has not been established, and signaling pathways are yet to be deciphered. We show that inhibiting TRPM7 channel-kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells results in reduced constitutive COX-2 expression. By utilizing a CML-derived cell line, HAP1, harboring CRISPR/Cas9-mediated TRPM7 knockout, or a point mutation inactivating TRPM7 kinase, we could link this to reduced activation of AKT serine/threonine kinase and mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2 (SMAD2). We identified AKT as a direct in vitro substrate of TRPM7 kinase. Pharmacologic blockade of TRPM7 in wildtype HAP1 cells confirmed the effect on COX-2 via altered AKT signaling. Addition of an AKT activator on TRPM7 kinase-dead cells reconstituted the wildtype phenotype. Inhibition of TRPM7 resulted in reduced phosphorylation of AKT and diminished COX-2 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells derived from CML patients, and reduced proliferation in patient-derived CD34+ cells. These results highlight a role of TRPM7 kinase in AKT-driven COX-2 expression and suggest a beneficial potential of TRPM7 blockade in COX-2-related inflammation and malignancy.
Keywords: AKT signaling; CML; COX-2; TRPM7; channel-kinase.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of financial interests. S.Z. holds the position of Editorial Board Member for FUNCTION and is blinded from reviewing or making decisions for the manuscript.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
