Normative data for paediatric lymphocyte subsets: A pilot study from western India
- PMID: 37787259
- PMCID: PMC10645029
- DOI: 10.4103/ijmr.ijmr_3282_21
Normative data for paediatric lymphocyte subsets: A pilot study from western India
Abstract
Background & objectives: Accurate diagnosis of immunodeficiencies requires a critical comparison of values with age-matched controls. In India, the existing reference values for rare lymphocyte subsets are currently not available and we rely on the data originating from other countries for the interpretation of the results. Furthermore, there is limited information on normal variation for these rare-subset parameters in Indian children. So, this study aimed to establish normative values for clinically important lymphocyte subsets in Indian children at different age groups.
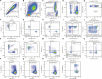
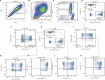
Methods: 148 children aged ≥16 yr were enrolled in this study. The study population included 61 per cent males and 39 per cent females and was divided into the following groups: cord blood (n=18), 0-6 months (n=9), 6-12 months (n=13), 1-2 yr (n=19), 2-5 yr (n=27), 5-10 yr (n=25) and 10-16 yr (n=37). The absolute and relative percentage of lymphocytes, T, B, natural killer cell, along with activated, naïve and memory subsets, was determined by flow cytometry.
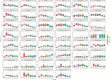
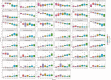
Results: Median values and the 10th and 90th percentiles were obtained for 34 lymphocyte sub-populations. The T and B naïve compartments showed a decreasing trend, whereas memory cells showed an increase with age. The activated T cell subset shows an increasing pattern up to one year and then declines gradually. Double negative T cells are relatively stable. TCRgd+T cell percentage increases with age.
Interpretation & conclusions: This single-centre pilot study provides preliminary data that justifies the need for future large-scale multi centric studies to generate a reference range for interpreting extended immunophenotyping profiles in the paediatric age group, making it possible for clinicians to assess the immunological status in inborn errors of immunity, infectious and autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: Children; flow cytometry; lymphocyte subset; pilot study; primary immunodeficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Garcia-Prat M, Álvarez-Sierra D, Aguiló-Cucurull A, Salgado-Perandrés S, Briongos-Sebastian S, Franco-Jarava C, et al. Extended immunophenotyping reference values in a healthy pediatric population. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2019;96:223–33. - PubMed
-
- Sack U, Gerling F, Tárnok A. Age-related lymphocyte subset changes in the peripheral blood of healthy children –A meta-study. Transfus Med Hemother. 2007;34:176–81.
-
- Zhang K, Wang F, Zhang M, Cao X, Yang S, Jia S, et al. Reference ranges of lymphocyte subsets balanced for age and gender from a population of healthy adults in Chongqing District of China. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2016;90:538–42. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
