Trend analysis of asthma mortality and years of life lost from 2004 to 2019 in Southern Iran
- PMID: 37787353
- PMCID: PMC10553790
- DOI: 10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_530_22
Trend analysis of asthma mortality and years of life lost from 2004 to 2019 in Southern Iran
Abstract
Objective: Asthma is a globally important non-communicable disease with major public health consequences. The aim of this study was to determine the mortality rate and years of life lost (YLL) due to asthma in southern Iran.
Methods: All deaths due to asthma in Fars province from the electronic population-based death registration system (EDRS) were obtained. Crude mortality rate, age-standardized mortality rate, YLL and YLL rate data were calculated. The JoinPoint Regression method was used to examine the trend.
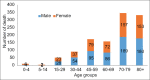
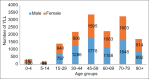
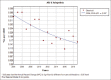
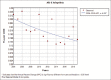
Results: During the 16-year study period (2004-2019), 1167 deaths due to asthma occurred in Fars province among which 54.7% (638 cases) were men and 29.6% (346 cases) were in the age group of 70-79 years. Crude mortality rate of asthma had decreased by 121% and 84% in males and females, respectively from 2004 to 2019. The total years of life lost due to asthma during the 16-year study period were 7697 (0.24 per 1000 people) in men, 6882 (0.22 per 1000 people) in women. According to the join point regression analysis, the 16-year trend of YLL rate due to premature mortality was decreasing: the annual percent change (APC) was -5.6% (95% CI -8.2 to -2.9, P = 0.001) for males, -4.4% (95% CI -7.3 to -1.4, P = 0.008) for females.
Conclusion: The trend of mortality and years of life lost due to asthma has decreased significantly during the years of study, although in some age groups, especially the age group of 45-59 years which has the highest number of years of life lost, this trend has been constant and unchanged. It is necessary to conduct other studies to investigate the possible reasons for this unchanged trend in vulnerable age groups.
Keywords: Asthma; Iran; joinpoint regression; mortality rate; trend; years of life lost.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trend Analysis of Leukemia Mortality and Years of Life Lost (YLL) from 2004 to 2019 in the Fars Province, Iran.Arch Iran Med. 2023 Oct 1;26(10):547-553. doi: 10.34172/aim.2023.80. Arch Iran Med. 2023. PMID: 38310410 Free PMC article.
-
Trend Analysis of Unintentional Fall Mortality and Years of Life Lost in the Fars Province of Iran, 2004-2019.Iran J Public Health. 2024 Jun;53(6):1427-1436. Iran J Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39430156 Free PMC article.
-
Trend of Mortality Rate and Years of Life Lost due to Cerebrovascular Diseases in Fars Province, Iran (2004-2019).Arch Iran Med. 2023 Apr 1;26(4):198-204. doi: 10.34172/aim.2023.30. Arch Iran Med. 2023. PMID: 38301079 Free PMC article.
-
The burden of premature mortality from cardiovascular diseases: A systematic review of years of life lost.PLoS One. 2023 Apr 21;18(4):e0283879. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283879. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37083866 Free PMC article.
-
[SENTIERI - Epidemiological Study of Residents in National Priority Contaminated Sites. Sixth Report].Epidemiol Prev. 2023 Jan-Apr;47(1-2 Suppl 1):1-286. doi: 10.19191/EP23.1-2-S1.003. Epidemiol Prev. 2023. PMID: 36825373 Italian.
References
-
- Stern J, Pier J, Litonjua AA. Asthma epidemiology and risk factors. Semin Immunopathol. 2020;42:5–15. - PubMed
-
- Croisant S. Epidemiology of asthma: Prevalence and burden of disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014:17–29. - PubMed
-
- Asher MI, García-Marcos L, Pearce NE, Strachan DP. Trends in worldwide asthma prevalence. Eur Respir J. 2020;56:2002094. doi:10.1183/13993003.02094-2020. - PubMed
-
- Varmaghani M, Farzadfar F, Sharifi F, Rashidian A, Moin M, Moradi-Lakeh M, et al. Prevalence of asthma, COPD, and chronic bronchitis in Iran: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016;15:93–104. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources