Global and regional quality of care index (QCI) by gender and age in oesophageal cancer: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 1990-2019
- PMID: 37788249
- PMCID: PMC10547202
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292348
Global and regional quality of care index (QCI) by gender and age in oesophageal cancer: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 1990-2019
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to examine the quality of care by age and gender in oesophageal cancer using Global Burden of Disease (GBD) database.
Methods: Patients aged 20 and over with oesophageal cancer were included in this longitudinal study using GBD 1990-2019 data. We used the Socio-Demographic Index (SDI) to classify the regions. We used Principal Component Analysis (PCA) method to calculate the Quality of Care Index (QCI). The QCI was rescaled into a 0-100 single index, demonstrating that the higher the score, the better the QC.
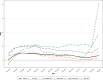
Results: The age-standardized QCI for oesophageal cancer dramatically increased from 23.5 in 1990 to 41.1 in 2019 for both sexes, globally. The high SDI regions showed higher QCI than the rest of the regions (45.1 in 1990 and 65.7 in 2019) whereas the low SDI regions had the lowest QCI, which showed a 4.5% decrease through the years (from 13.3 in 1990 to 12.7 in 2019). Globally, in 2019, the QCI showed the highest scores for patients aged 80-84, reported 48.2, and the lowest score for patients aged 25-29 reported 31.5, for both sexes. Globally, in 2019, age-standardized Gender Disparity Ratio (GDR) was 1.2, showing higher QCI in females than males.
Conclusion: There were fundamental differences in the QCI both globally and regionally between different age groups as well as between males and females. To achieve the goal of providing high-quality services equally to people in need in all over the world, health systems need to invest in effective diagnostic services, treatments, facilities, and equipment and to plan for screening and surveillance of high-risk individuals.
Copyright: © 2023 Iezadi et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Institutional Agency for Research On Cancer. Oesophagus: World Health Organization (WHO); 2020 [cited 2021]. Available from: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home.
-
- Mohammadi E, Ghasemi E, Azadnajafabad S, Rezaei N, Saeedi Moghaddam S, Ebrahimi Meimand S, et al.. A global, regional, and national survey on burden and Quality of Care Index (QCI) of brain and other central nervous system cancers; global burden of disease systematic analysis 1990–2017. PLOS ONE. 2021;16(2):e0247120. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247120 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

