Validity and reliability of the international physical activity questionnaire short form in Chilean adults
- PMID: 37788251
- PMCID: PMC10547187
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291604
Validity and reliability of the international physical activity questionnaire short form in Chilean adults
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to determine the test-retest reliability and concurrent validity of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire Short Form (IPAQ-SF) in Chilean adults.
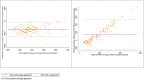
Methods: A cross-sectional validation study was carried out on 161 adults aged between 35 and 65, selected from a population-based study in Temuco, Chile. IPAQ-SF was completed twice, seven days apart, to analyze the test-retest reliability with the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). Objective PA was assessed by accelerometry (ActiGraph GT3X+) for seven consecutive days. Intraclass correlation coefficients were used to determine the reliability. Spearman correlation coefficients (rho) and Bland-Altman plots were calculated to assess validity.
Results: 144 subjects (52.5 ± 8.8 years, 53.9% men) answered the IPAQ-SF on both occasions and had valid accelerometry data. The IPAQ-SF showed moderate reliability for sitting time (ICC = 0.62), while it was poor for walking (ICC = 0.40), moderate PA (ICC = 0.41), vigorous PA (ICC = 0.48), and total PA (ICC = 0.33). There were weak correlations between IPAQ-SF and accelerometry for sedentary behavior (rho = 0.28, p = 0.0005), walking (rho = 0.11, p = 0.17), moderate PA (rho = 0.13, p = 0.128), vigorous PA (rho = 0.18, p = 0.03), and total PA (rho = 0.26, p = 0.002).
Conclusions: The results suggest that the IPAQ-SF test and retest would provide an acceptable measure of total SB and MVPA, and a weak correlation between IPAQ-SF and accelerometer.
Copyright: © 2023 Balboa-Castillo et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validity and reliability of International Physical Activity Questionnaire-Short Form in Chinese youth.Res Q Exerc Sport. 2013 Dec;84 Suppl 2:S80-6. doi: 10.1080/02701367.2013.850991. Res Q Exerc Sport. 2013. PMID: 24527570
-
Concurrent validity between self-reported International Physical Activity Questionnaire Short Form and Fibion accelerometer data among young adults in the UAE.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Aug 19;29(1):426. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01975-5. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39155363 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of physical activity in older Belgian adults: validity and reliability of an adapted interview version of the long International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ-L).BMC Public Health. 2015 Apr 28;15:433. doi: 10.1186/s12889-015-1785-3. BMC Public Health. 2015. PMID: 25928561 Free PMC article.
-
Self-administered physical activity questionnaires for the elderly: a systematic review of measurement properties.Sports Med. 2010 Jul 1;40(7):601-23. doi: 10.2165/11531350-000000000-00000. Sports Med. 2010. PMID: 20545382
-
Reliability and Convergent Validity of Self-Reported Physical Activity Questionnaires for People With Mental Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Phys Act Health. 2021 Jan 1;18(1):109-115. doi: 10.1123/jpah.2020-0312. Epub 2020 Dec 1. J Phys Act Health. 2021. PMID: 33260145
Cited by
-
Association of sleep hygiene knowledge and physical activity with sleep quality in nursing and medical students: a cross-sectional study.Front Sports Act Living. 2025 Mar 20;7:1453404. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2025.1453404. eCollection 2025. Front Sports Act Living. 2025. PMID: 40181932 Free PMC article.
-
Brain basis for physical activity levels mediate beta Inhibition to improve cognitive function in elderly based on multimodality monitoring.Sci Rep. 2025 May 23;15(1):17937. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98857-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40410437 Free PMC article.
-
Healthy Lifestyle Related to Executive Functions in Chilean University Students: A Pilot Study.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 May 15;12(10):1022. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12101022. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38786435 Free PMC article.
-
Postacute Myocardial Infarction Differences in Physical Activity Behavior, Anxiety, and Depression Levels.SAGE Open Nurs. 2024 Dec 23;10:23779608241304478. doi: 10.1177/23779608241304478. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. SAGE Open Nurs. 2024. PMID: 39734763 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Response After a Single Maximal Exercise Session in Physically Inactive Young Adults (EASY Study): Relevancy of Adiponectin Isoforms.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 20;15(3):314. doi: 10.3390/biom15030314. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40149850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wannamethee SG, Shaper AG. Physical activity in the prevention of cardiovascular disease: an epidemiological perspective. Sports Med. 2001;31: 101–14. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11227978 doi: 10.2165/00007256-200131020-00003 - DOI - PubMed