Antioxioxidant and antiapoptotic effects of Thymosin β4 in Aβ-induced SH-SY5Y cells via the 5-HTR1A/ERK axis
- PMID: 37788276
- PMCID: PMC10547165
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287817
Antioxioxidant and antiapoptotic effects of Thymosin β4 in Aβ-induced SH-SY5Y cells via the 5-HTR1A/ERK axis
Abstract
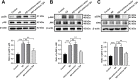
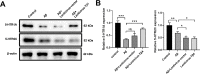
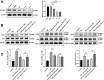
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a common amnestic cognitive impairment characterised by β-amyloid (Aβ) plaques deposit in the brain of the elderly. AD is a yet incurable disease due to its unknown exact pathogenesis and unavailability of effective remedies in clinical application. Thymosin β4 (Tβ4) is a housekeeping protein that plays important role in cell proliferation, migration and differentiation. It has the ability to protect and repair neurons however it is still unclear involvement in AD. Therefore, the aim of this study is to elucidate the role and mechanism of Tβ4 in mediating the improvement of AD. AD-like cell model was constructed in neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y treated with Aβ. Overexpression of Tβ4 were done using lentivirus infection and downregulation through siRNA transfection. We performed western blot and flow cytometry to study the apoptosis and standard kits to measure the oxidative stress-associated biomarkers. There is significant increased in viability and decreased apoptosis in Tβ4 overexpression group compared to control. Furthermore, overexpression of Tβ4 suppressed the expression of pro-apoptotic markers such as Caspase-3, Caspase-8, and Bax meanwhile upregulated the expression of anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2. Tβ4 alleviated oxidative damage by reducing MDA, LDH and ROS and increasing SOD and GSH-PX in Aβ-treated SH-SY5Y cells. We found that Tβ4 inhibit ERK/p38 MAPK pathway and intensify the expression of 5-HTR1A. Additionally, we showed that upregulation of 5-HTR1A dampened the Tβ4 to activate ERK signalling. In conclusion, our study revealed the neuroprotective role of Tβ4 in AD which may open up new therapeutic applications in AD treatment.
Copyright: © 2023 Zhang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tβ4 ameliorates oxidative damage and apoptosis through ERK/MAPK and 5-HT1A signaling pathway in Aβ insulted SH-SY5Y cells.Life Sci. 2021 Nov 25:120178. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.120178. Online ahead of print. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34838849
-
[Effect and mechanism of thymosin beta 4 on spinal cord-derived neural stem /progenitor cell injury induced by oxidative stress].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2022 Aug 25;35(8):763-71. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.2022.08.012. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2022. PMID: 35979771 Chinese.
-
Thymosin β4 reverses phenotypic polarization of glial cells and cognitive impairment via negative regulation of NF-κB signaling axis in APP/PS1 mice.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Jun 28;18(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02166-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34183019 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potentials of plant iridoids in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 1;169:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30877973 Review.
-
Thymosin beta4 in multiple myeloma: friend or foe.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Apr;1194:125-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05470.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20536459 Review.
Cited by
-
Different amyloid β42 preparations induce different cell death pathways in the model of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Nov 17;29(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00657-8. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39551742 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydroergotamine and Bromocriptine: Potential Drugs for the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder and Alzheimer's Disease Comorbidity.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Feb;62(2):2493-2514. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04416-w. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39134826
References
-
- Ismail Z, Gatchel J, Bateman DR, Barcelos-Ferreira R, Cantillon M, Jaeger J, et al.. Affective and emotional dysregulation as pre-dementia risk markers: exploring the mild behavioral impairment symptoms of depression, anxiety, irritability, and euphoria. International psychogeriatrics. 2018;30(2):185–96. doi: 10.1017/S1041610217001880 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nguyen PH, Ramamoorthy A, Sahoo BR, Zheng J, Faller P, Straub JE, et al.. Amyloid oligomers: A joint experimental/computational perspective on Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, type II diabetes, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Chemical reviews. 2021;121(4):2545–647. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01122 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

