Overexpression of Human Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Exacerbates Coronary Reactive Hyperemia Reduction in Angiotensin-II-Treated Mouse Hearts
- PMID: 37788350
- PMCID: PMC10841723
- DOI: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001490
Overexpression of Human Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Exacerbates Coronary Reactive Hyperemia Reduction in Angiotensin-II-Treated Mouse Hearts
Abstract
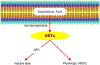
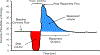
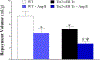
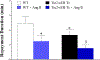
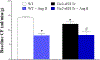
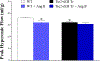
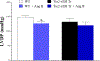
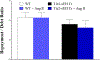
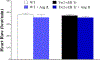
Coronary reactive hyperemia (CRH) is impaired in cardiovascular diseases, and angiotensin-II (Ang-II) exacerbates it. However, it is unknown how Ang-II affects CRH in Tie2-sEH Tr (human-sEH-overexpressed) versus wild-type (WT) mice. sEH-overexpression resulted in CRH reduction in Tie2-sEH Tr versus WT. We hypothesized that Ang-II exacerbates CRH reduction in Tie2-sEH Tr versus WT. The Langendorff system measured coronary flow in Tie2-sEH Tr and WT. The hearts were exposed to 15-second ischemia, and CRH was assessed in 10 mice each. Repayment volume was reduced by 40.50% in WT treated with Ang-II versus WT (7.42 ± 0.8 to 4.49 ± 0.8 mL/g) and 48% in Tie2-sEH Tr treated with Ang-II versus Tie2-sEH Tr (5.18 ± 0.4 to 2.68 ± 0.3 mL/g). Ang-II decreased repayment duration by 50% in WT-treated with Ang-II versus WT (2.46 ± 0.5 to 1.24 ± 0.4 minutes) and 54% in Tie2-sEH Tr treated with Ang-II versus Tie2-sEH Tr (1.66 ± 0.4 to 0.76 ± 0.2 minutes). Peak repayment flow was reduced by 11.2% in WT treated with Ang-II versus WT (35.98 ± 0.7 to 32.11 ± 1.4 mL/g) and 4% in Tie2-sEH Tr treated with Ang-II versus Tie2-sEH Tr (32.18 ± 0.6 to 30.89 ± 1.5 mL/g). Furthermore, coronary flow was reduced by 43% in WT treated with Ang-II versus WT (14.2 ± 0.5 to 8.15 ± 0.8 mL/min/g) and 32% in Tie2-sEH Tr treated with Ang-II versus Tie2-sEH Tr (12.1 ± 0.8 to 8.3 ± 1.2 mL/min/g). Moreover, the Ang-II-AT 1 -receptor and CYP4A were increased in Tie2-sEHTr. Our results demonstrate that Ang-II exacerbates CRH reduction in Tie2-sEH Tr mice.
Copyright © 2023 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
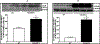
References
-
- Hanif A, Edin ML, Zeldin DC, Morisseau C, Falck JR, Ledent C, Tilley SL, Nayeem MA. Reduced coronary reactive hyperemia in mice was reversed by the soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor (t-AUCB): Role of adenosine A2A receptor and plasma oxylipins. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017. Jul;131:83–95. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

