Advances and Challenges in Molecular Imaging of Viral Infections
- PMID: 37788495
- PMCID: PMC10547465
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiad247
Advances and Challenges in Molecular Imaging of Viral Infections
Abstract
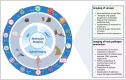
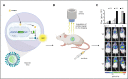
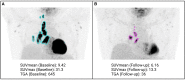
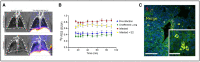
Molecular imaging of viral infection, using a variety of advanced imaging techniques such as optical and nuclear imaging, can and has been used for direct visualization of the virus as well as assessment of virus-host interactions. Unlike imaging of other pathogens such as bacteria and fungi, challenging aspects of imaging viral infections include the small size of viruses, the complexity of viral infection animal models (eg, species dependence), and the high-level containment needs for many high-consequence pathogens, among others. In this review, using representative viral infections, we discuss how molecular imaging can reveal real-time infection dynamics, improve our understanding of disease pathogenesis, and guide optimization of treatment and prevention strategies. Key findings from human and animal studies are highlighted.
Keywords: Ebola; HIV; PET scan; RSV; high-consequence infection; influenza; molecular imaging; reporter virus; viral infection.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest. All authors: No reported conflicts of interest. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modeling Host-Virus Interactions in Viral Infectious Diseases Using Stem-Cell-Derived Systems and CRISPR/Cas9 Technology.Viruses. 2019 Jan 30;11(2):124. doi: 10.3390/v11020124. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30704043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accelerated viral dynamics in bat cell lines, with implications for zoonotic emergence.Elife. 2020 Feb 3;9:e48401. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48401. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32011232 Free PMC article.
-
CT of viral lower respiratory tract infections in adults: comparison among viral organisms and between viral and bacterial infections.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011 Nov;197(5):1088-95. doi: 10.2214/AJR.11.6501. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011. PMID: 22021500
-
Community respiratory viruses in individuals with human immunodeficiency virus infection.Am J Med. 1997 Mar 17;102(3A):19-24; discussion 25-6. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(97)80005-8. Am J Med. 1997. PMID: 10868138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virus-Host Interactions: New Insights and Advances in Drug Development Against Viral Pathogens.Curr Drug Metab. 2017;18(10):942-970. doi: 10.2174/1389200218666170925115132. Curr Drug Metab. 2017. PMID: 28952435 Review.
Cited by
-
Reactive oxygen species-related oxidative changes are associated with splenic lymphocyte depletion in Ebola virus infection.Npj Imaging. 2025;3(1):16. doi: 10.1038/s44303-025-00079-x. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Npj Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40291761 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring RVFV Infection Using Bioluminescent Reporter Viruses In Vivo.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2824:447-459. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3926-9_28. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39039429
-
Nuclear Medicine Imaging Tools in Fever of Unknown Origin: Time for a Revisit and Appropriate Use Criteria.Clin Infect Dis. 2024 May 15;78(5):1148-1153. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciae115. Clin Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38441140 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular imaging of viral pathogenesis and opportunities for the future.Npj Imaging. 2025;3(1):3. doi: 10.1038/s44303-024-00056-w. Epub 2025 Jan 24. Npj Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39872292 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alauddin MM, Gelovani JG. Radiolabeled nucleoside analogues for PET imaging of HSV1-tk gene expression. Curr Top Med Chem 2010; 10:1617–32. - PubMed
-
- Luker GD, Luker KE, Sharma V, et al. . In vitro and in vivo characterization of a dual-function green fluorescent protein–HSV1-thymidine kinase reporter gene driven by the human elongation factor 1 alpha promoter. Mol Imaging 2002; 1:65–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

