A Phase 3, randomized, non-inferiority study of a heterologous booster dose of SARS CoV-2 recombinant spike protein vaccine in adults
- PMID: 37789040
- PMCID: PMC10547846
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-43578-w
A Phase 3, randomized, non-inferiority study of a heterologous booster dose of SARS CoV-2 recombinant spike protein vaccine in adults
Abstract
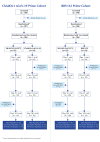
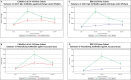
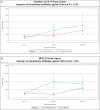
Due to waning immunity following primary immunization with COVID-19 vaccines, booster doses may be required. The present study assessed a heterologous booster of SII-NVX-CoV2373 (spike protein vaccine) in adults primed with viral vector and inactivated vaccines. In this Phase 3, observer-blind, randomized, active controlled study, a total of 372 adults primed with two doses of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (n = 186) or BBV152 (n = 186) at least six months ago, were randomized to receive a booster of SII-NVX-CoV2373 or control vaccine (homologous booster of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 or BBV152). Anti-S IgG and neutralizing antibodies (nAbs) were assessed at days 1, 29, and 181. Non-inferiority (NI) of SII-NVX-CoV2373 to the control vaccine was assessed based on the ratio of geometric mean ELISA units (GMEU) of anti-S IgG and geometric mean titers (GMT) of nAbs (NI margin > 0.67) as well as seroresponse (≥ 2 fold-rise in titers) (NI margin -10%) at day 29. Safety was assessed throughout the study period. In both the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 prime and BBV152 prime cohorts, 186 participants each received the study vaccines. In the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 prime cohort, the GMEU ratio was 2.05 (95% CI 1.73, 2.43) and the GMT ratio was 1.89 (95% CI 1.55, 2.32) whereas the difference in the proportion of seroresponse was 49.32% (95% CI 36.49, 60.45) for anti-S IgG and 15% (95% CI 5.65, 25.05) for nAbs on day 29. In the BBV152 prime cohort, the GMEU ratio was 5.12 (95% CI 4.20, 6.24) and the GMT ratio was 4.80 (95% CI 3.76, 6.12) whereas the difference in the proportion of seroresponse was 74.08% (95% CI 63.24, 82.17) for anti-S IgG and 24.71% (95% CI 16.26, 34.62) for nAbs on day 29. The non-inferiority of SII-NVX-CoV2373 booster to the control vaccine for each prime cohort was met. SII-NVX-CoV2373 booster showed significantly higher immune responses than BBV152 homologous booster. On day 181, seroresponse rates were ≥ 70% in all the groups for both nAbs and anti-S IgG. Solicited adverse events reported were transient and mostly mild in severity in all the groups. No causally related SAE was reported. SII-NVX-CoV2373 as a heterologous booster induced non-inferior immune responses as compared to homologous boosters in adults primed with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BBV152. SII-NVX-CoV2373 showed a numerically higher boosting effect than homologous boosters. The vaccine was also safe and well tolerated.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
PSK, BG, CB, DK, AD, MG and US are employees of SIIPL. JSP, MZ, RK and SCC are employees of Novavax Inc. CSP is Chairman and Managing Director of SIIPL. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/ Accessed 08 December 2022.
-
- https://covid19.who.int/region/searo/country/in Accessed 08 Dec 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

