Focal ischemic stroke modifies microglia-derived exosomal miRNAs: potential role of mir-212-5p in neuronal protection and functional recovery
- PMID: 37789455
- PMCID: PMC10548705
- DOI: 10.1186/s40659-023-00458-x
Focal ischemic stroke modifies microglia-derived exosomal miRNAs: potential role of mir-212-5p in neuronal protection and functional recovery
Abstract
Background: Ischemic stroke is a severe type of stroke with high disability and mortality rates. In recent years, microglial exosome-derived miRNAs have been shown to be promising candidates for the treatment of ischemic brain injury and exert neuroprotective effects. Mechanisms underlying miRNA dysregulation in ischemic stroke are still being explored. Here, we aimed to verify whether miRNAs derived from exosomes exert effects on functional recovery.
Methods: MiR-212-5p agomir was employed to upregulate miR-212-5p expression in a rat model of middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion (MCAO/R) as well as an oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) in vitro. Western blot analysis, qRT-PCR and immunofluorescence staining and other methods were applied to explore the underlying mechanisms of action of miR-212-5p.
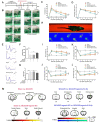
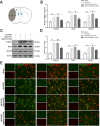
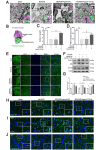
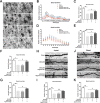
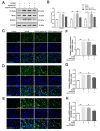
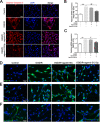
Results: The results of our study found that intervention with miR-212-5p agomir effectively decreased infarct volume and restored motor function in MCAO/R rats. Mechanistically, miR-212-5p agomir significantly reduced the expression of PlexinA2 (PLXNA2). Additionally, the results obtained in vitro were similar to those achieved in vivo.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the present study indicated that PLXNA2 may be a target gene of miR-212-5p, and miR-212-5p has great potential as a target for the treatment and diagnosis of ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Exosomal; Ischemic stroke; MiR-212-5p; Microglial; Neuronal protection; PlexinA2.
© 2023. Sociedad de Biologia de Chile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2018YFC2001600, and 2018YFC2001604/the National Key R&D Program of China
- 81802249/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81871836/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81874035/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81902301/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 18511108300, 18441903900, and 18441903800/Shanghai Science and Technology Committee
- 19QA1409000/Shanghai Rising-Star Program
- 2018YQ02, and 201840224/Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning
- RY411.19.01.10/Shanghai Youth Top Talent Development Plan and Shanghai Rising Stars of Medical Talent Youth Development Program
- 19XD1403600/Program of Shanghai Academic Research Leader
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

