A Neuro-Ophthalmologist's Guide to Advances in Intracranial Pressure Measurements
- PMID: 37790122
- PMCID: PMC10543929
- DOI: 10.2147/EB.S404642
A Neuro-Ophthalmologist's Guide to Advances in Intracranial Pressure Measurements
Abstract
Cerebrospinal fluid disorders have a wide-ranging impact on vision, headache, cognition and a person's quality of life. Due to advances in technology and accessibility, intracranial pressure measurement and monitoring, usually managed by neurosurgeons, are being employed more widely in clinical practice. These developments are of direct importance for Ophthalmologists and Neurologists because the ability to readily measure intracranial pressure can aide management decisions. The aim of this review is to present the emerging evidence for intracranial pressure measurement methods and interpretation that is relevant to Neuro-ophthalmologists.
Keywords: cerebrospinal fluid; intracranial pressure; intraparenchymal intracranial pressure sensors; lumbar puncture opening pressure; neuro-ophthalmology; non-invasive; pseudotumour cerebri; telemetric intracranial pressure monitor; waveform.
© 2023 Mollan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Professor Alexandra Sinclair reports personal fees from Invex therapeutics in her role as Director with stock holdings. Honoria from Allergan, Novartis, Chiesi and Amgen outside the submitted work. Professor Susan Mollan has received honoraria for speaker events from AbbVie, Heidelberg engineering, Chugai-Roche Ltd and Teva. Honoraria for advisory boards for Invex Therapeutics, Gensight and ocular therapeutix. Consultancy fees from the Velux foundation, Neurodiem and Invex Therapeutics. She also reports grants from National institute of health research and UK space agency. Ms Olivia Grech reports scientific consultancy fee from Index Therapeutics. Professor Alex Sinclair owns shares from Invex Therapeutics. Dr Georgios Tsermoulas was an invited speaker to a “lunch symposium” sponsored by Braun in the Hydrocephalus 2022 meeting in Gothenburg on Mon 12th Sep 2022 and presented on “Intracranial pressure recordings in shunted patients with Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension”. However, he did not receive any remuneration or any other benefits in relation to this presentation. All declared interested are outside the area of this submitted work. All other authors declare no competing interests in this work.
Figures
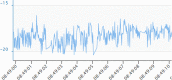
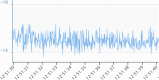
References
-
- Loman J, Myerson A, Goldman D. Effects of alterations in posture on the cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Arch Neur Psych. 1935;33:1279–1295. doi:10.1001/archneurpsyc.1935.02250180138007 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

